Search Results for: chlorophyll a
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Chlorophyll a
Definition noun A type of chlorophyll that is most common and predominant in all oxygen-evolving photosynthetic organisms... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
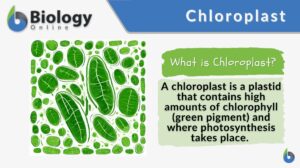
Chloroplast
Chloroplast Definition What is chloroplast? In biology, a chloroplast refers to the organelle found within the cell of... Read More
Chlorophyll c
Definition noun A form of chlorophyll that occurs only in algae, specifically the diatoms, dinoflagellates and brown algae.... Read More
Chlorophyll d
Definition noun A type of chlorophyll found in marine red algae and cyanobacteria, and absorbs the infrared light of the... Read More
Chlorophyll e
Definition noun A rare type of chlorophyll isolated from the two algae, Tribonema bombycinum and Vaucheria... Read More
Charophyta
Charophyta is a taxonomic group (a phylum) comprised of green algae that live predominantly in freshwater habitats. Members... Read More
Green algae
Green Algae Definition Green algae (singular: green alga) are photosynthetic algae that are characterized by having... Read More
Dinoflagellate
A dinoflagellate is a flagellate algae characterized by their two flagella of unequal length. One of the flagella is lying... Read More
Accessory pigment
Definition noun, plural: accessory pigments A non-chlorophyll pigment inside the chloroplast of photosynthetic organisms,... Read More
Brown algae
Brown Algae Definition Brown algae are algal species characterized by being multicellular and having a brown or... Read More
Phycobilin
Definition noun, plural: phycobilins A water-soluble accessory pigment found in red algae and... Read More
Xanthophyceae
Definition noun A taxonomic class comprised of the xanthophytes (yellow-green algae) Supplement Xanthophyceae is a taxonomic... Read More
Carotenoid
Definition noun, plural: carotenoids (botany) Any of the pigment molecules, typically yellow, red, and orange, that interact... Read More
Photolysis
Photolysis Definition We define photolysis as a chemical process in which chemical compounds or molecules are split into... Read More
Microalgae
Microalgae Definition Microalgae (singular: microalga) are microscopic algal species as opposed to other algae that are... Read More
Fucoxanthin
Fucoxanthin (Science: chemical) carotenoid pigment of certain brown algae (Phaeophyta) and bacteria: absorbs at 500-580... Read More
Light reactions
Definition noun The series of biochemical reactions in photosynthesis that require light energy that is captured by... Read More
photobiology
Photobiology Definition Photobiology, the biology of light, is a subdiscipline in biology. It focuses on the effects of... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Chlorenchyma
Definition noun A parenchyma cell with chloroplasts, and is therefore photosynthetic Supplement Vascular plants are... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More
Reaction centre
reaction centre (Science: plant biology) The site in the chloroplast that receives the energy trapped by chlorophyll and... Read More