Search Results for: chloroplast
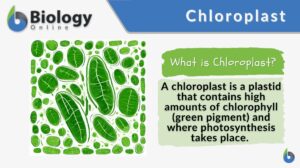
Chloroplast
Chloroplast Definition What is chloroplast? In biology, a chloroplast refers to the organelle found within the cell of... Read More
Chloroplast DNA
Definition noun plural: chloroplast DNAs DNA in the chloroplast that carries the code for proteins and RNAs essential to... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
Gerontoplast
Definition noun, plural: gerontoplasts A plastid that forms from chloroplast during senescence Supplement Plastids are... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Chlorenchyma
Definition noun A parenchyma cell with chloroplasts, and is therefore photosynthetic Supplement Vascular plants are... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Proplastid
Definition noun, plural: proplastids A small, colourless organelle that gives rise to a plastid (e.g. chloroplast,... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Dinoflagellate
A dinoflagellate is a flagellate algae characterized by their two flagella of unequal length. One of the flagella is lying... Read More
Chromoplast
Definition noun, plural: chromoplasts Any of the coloured plastids associated with pigment synthesis and... Read More
Leucoplast
Definition noun, plural: leucoplasts A plastid lacking photosynthetic pigments and involved in various biosynthetic... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More
Elaioplast
Definition noun, plural: elaioplasts (botany) A leucoplast that stores oil Supplement Plastids are organelles involved in... Read More
Chlorophyta
Chlorophyta Definition Chlorophyta is a taxonomic group (a phylum) comprised of green algae that live in marine habitats.... Read More
Carotenoid
Definition noun, plural: carotenoids (botany) Any of the pigment molecules, typically yellow, red, and orange, that interact... Read More
Phycobilin
Definition noun, plural: phycobilins A water-soluble accessory pigment found in red algae and... Read More
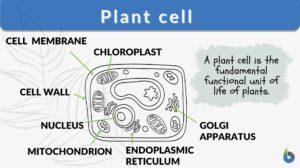
Plant cell
Plant Cell Definition A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant... Read More
Accessory pigment
Definition noun, plural: accessory pigments A non-chlorophyll pigment inside the chloroplast of photosynthetic organisms,... Read More
Cryptomonad
Definition noun, plural: cryptomonads Any of the species belonging to Phylum Cryptophyta, and characterized by being aquatic... Read More
Archaeplastida
Definition noun A taxonomic kingdom of the domain Eukaryota that includes land plants, green algae, red algae, and... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Proteinoplast
Definition noun, plural: proteinoplasts (botany) A leucoplast that stores and modifies protein Supplement Plastids are... Read More
Photosynthesis – Photolysis and Carbon Fixation
Photosynthesis is the means that primary producers (mostly plants) can obtain energy via light energy. The energy gained... Read More
Photolysis
Photolysis Definition We define photolysis as a chemical process in which chemical compounds or molecules are split into... Read More