Search Results for: concentration
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Concentration
Definition noun (1) The measure of the amount of a sub-component (especially solute) in a solution (2) The ratio of the mass... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
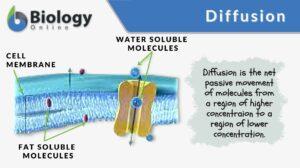
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
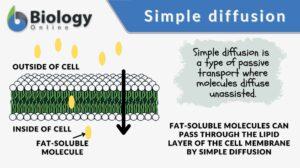
Simple diffusion
Diffusion is essential in the anatomy and physiology of a living thing, especially with regard to homeostasis. It is one of... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
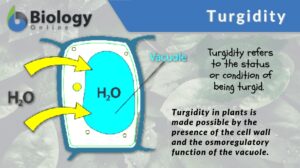
Plant Water Regulation
A plant requires water as an essential ingredient of photolysis, the photochemical stage of photosynthesis where water is... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Critical concentration
Critical concentration (Science: chemistry) The minimum concentration of units needed before a biological polymer will... Read More
Passive transport
Passive transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances such as ions and molecules move down their respective... Read More
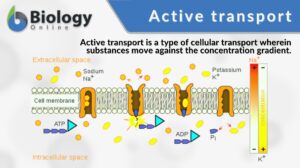
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma.Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
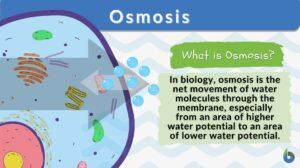
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More
Animal Water Regulation
Homeostatic control, a set environment, and how evolution and natural selection drives a species to adapt to its environment... Read More
Peak plasma drug concentration
peak plasma drug concentration (Science: pharmacology) The highest level of drug that can be obtained in the blood usually... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Apical Dominance
a condition where vertical growth supercedes lateral growth in a plant. this is controlled by auxins, where in high... Read More
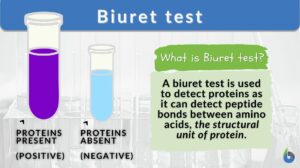
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. WrightDepartment of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Third-order kinetics
third-order kinetics (Science: pharmacology) A term describing the reaction rate of a chemical reaction in which the rate... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More

















![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)