Search Results for: critical concentration
Critical concentration
Critical concentration (Science: chemistry) The minimum concentration of units needed before a biological polymer will... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Concentration
Definition noun (1) The measure of the amount of a sub-component (especially solute) in a solution (2) The ratio of the mass... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. WrightDepartment of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
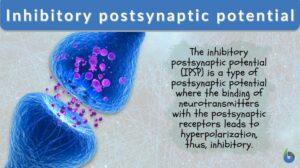
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
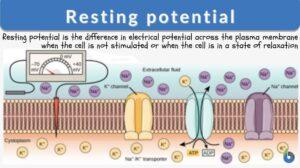
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Bolus injection
A bolus injection is the act of administering a dose of medication or substance directly into the bloodstream by injection.... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
Still Water Community Plants
Freshwater Plants & Water As mentioned in the previous tutorial about still water plants, the method of transpiration... Read More
Chemotaxis
Definition noun The directional movement of an organism or a living motile cell in response to certain diffusible chemicals... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Cork cambium
Cork Cambium Definition Cork cambium is a secondary meristematic tissue that has a pivotal role in secondary growth in... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More