Search Results for: dehydrogenase
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Dehydrogenase
Dehydrogenase (Science: enzyme) enzyme that oxidizes a substrate by transferring hydrogen to an acceptor that is either... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Androsterone
Definition noun, plural: androsterones A steroid hormone, with a chemical formula of C19H30O2, has masculinizing effects,... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
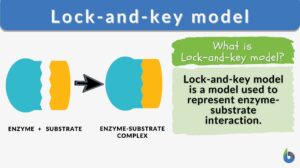
Lock-and-key model
Lock-and-key model Definition Lock-and-key model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
White adipose tissue
Definition noun, plural: white adipose tissues A type of adipose tissue found in mammals used to store energy and acts as... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Marker enzyme
Definition noun, plural: marker enzymes Any enzyme confined to a particular organelle, cell, or cellular... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Chromosomes X and Y and Sex Determination
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.In humans, the normal chromosome complement is 46, consisting of 22 pairs of... Read More
Thromboxane
Definition noun, plural: thromboxanes Any from the various arachidonic acid metabolites produced by the action of... Read More
Flavin mononucleotide
Definition noun plural: flavin mononucleotides fla·vin mon·o·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌmɒnəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Cytidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is composed of cytidine (a cytosine... Read More
Substrate specificity
Definition noun A feature of enzyme activity with regard to the kind of substrate reacting with an enzyme to yield a... Read More
Pentose phosphate pathway
Definition noun (biochemistry) A glucose metabolic pathway in which five-carbon sugars (pentoses) and NADPH are synthesized... Read More
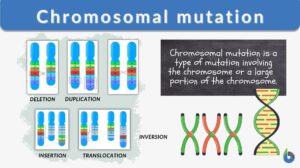
Chromosomal mutation
Every living thing is made up of DNA. Our DNA is what makes us unique and different in the world. Our DNA is made up of... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More