Search Results for: dense bodies
Dense bodies
Dense bodies (Science: cell biology) areas of electron density associated with the thin filaments in smooth muscle cells.... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Myoepithelial cell
Definition noun, plural: myoepithelial cells (1) (histology) A slender, spindle-shaped contractile cell forming the thin... Read More
Unstriated muscle
unstriated muscle --> smooth muscle (Science: anatomy, pathology, physiology) muscle tissue in vertebrates made up from... Read More
Nuclear lamina
Definition noun plural: nuclear laminae or nuclear laminas nu·cle·ar lam·i·na, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈlæm.ɪ.nə (cell... Read More
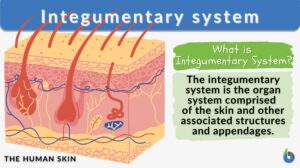
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Woolly cheetah
Woolly cheetahs were reported in the 19th century as a separate species of cheetah that had longer, denser fur. Several... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Lysosomal enzyme
Definition noun plural: lysosomal enzymes ly·so·somal en·zyme, ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm əl ˈɛnzaɪm (biochemistry) Any of... Read More
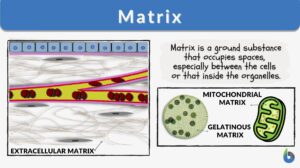
Nuclear matrix
Definition noun plural: nuclear matrices (cell biology) A 3-dimensional filamentous protein network that extends... Read More
Biodiversity
The biological world or life on earth is a marvel that has amazed us since time immemorial. The rich natural diversity of... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More