Search Results for: diarrhea
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
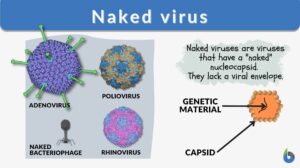
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More
Vibrio cholerae
Definition Noun A gram-negative single polar flagellum bacterium associated with cholera infection in... Read More
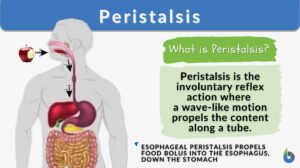
Peristalsis
What is Peristalsis? Peristalsis is the series of involuntary, wave-like muscle movements in the cylindrical, hollow tube... Read More
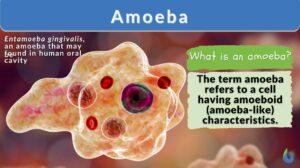
Entamoebidae
Definition noun (taxonomy) A family of Archamoebae which includes species such as Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba coli,... Read More
Isomaltose
Definition noun plural: isomaltoses i·so·mal·tose, aɪsoʊˈmɔːltəʊz A disaccharide formed from the combination of... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Archamoebae
Definition noun A taxonomic class in Phylum Amoebozoa characterized by the absence of mitochondria Supplement Archamoeba... Read More
Salmonella typhimurium
Definition A gram-negative pathogenic bacterium associated in gastroenteritis in humans and other... Read More
Lactobacillus casei
Definition noun A non-pathogenic and harmless bacterium recognized widely as probiotics that controls growth of various... Read More
Anhidrosis
Definition noun, plural: anhidroses A pathological condition characterized by the inability to sweat... Read More
Vermiform appendix
Definition noun, plural: vermiform appendixes (anatomy) A worm-shaped, vestigial process extending from the lower blind end... Read More
Balantidium coli
Definition noun A parasitic ciliate belonging to the family Balantiididae, and the causative agent of the balantidiasis... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Coprophagia
Definition noun The eating of feces Supplement Coprophagia refers to the eating of feces or excrement. It is also referred... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Enterococcus faecalis
Definition Non-motile, gram-positive, facultatively anaerobic, microbial species that normally dwells in the... Read More
Entamoeba histolytica
Definition noun A disease-causing anaerobic protozoan species capable of causing entamoebiasis and amebic dysentery to its... Read More
Disruptive Selection
An evolutionary process known as disruptive selection (or disruptive natural selection) causes a population to become... Read More
Necator americanus
Definition noun A parasitic worm of humans and other animals and is regarded as the New World hookworm Supplement Necator... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
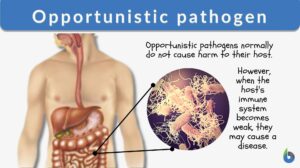
Opportunistic pathogen
Opportunistic Pathogen Definition How do we define opportunistic pathogen? The opportunistic pathogen is an infectious... Read More