Search Results for: element
Sieve element
Definition noun (botany) A food-conducting cell in the phloem of vascular plants Supplement The phloem is the vascular... Read More
Sieve-tube element
Definition noun, plural: sieve tube elements A specialized type of sclerenchyma cell that forms a sieve tube of... Read More
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
Noble element
noble element --> noble metal A metal that cannot be oxidised by heat alone, nor readily dissolved by acid; e.g., gold,... Read More
Enhancer element
Enhancer element (Science: molecular biology) a dna sequence, present in the genomes of higher eukaryotes and of various... Read More
Control element
Control element generic term for a region of dna, such as a promoter or enhancer adjacent to (or within) a gene that allows... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Sieve tube
Definition noun, plural: sieve tubes (botany) Any of the tubes in the phloem comprised of cells joined end-to-end through... Read More
Sieve cell
Definition noun, plural: sieve cells (botany) The main conductive cell in the phloem of the gymnosperms and... Read More
Companion cell
Definition noun (botany) Any of the metabolically-active parenchyma cells associated with a sieve tube element in the phloem... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Interspersed repeat
Definition noun, plural: interspersed repeats A type of repeated sequence in which the copies are dispersed throughout the... Read More
Genetic Engineering Advantages & Disadvantages
Through genetic engineering, scientists are able to move desirable genes from one plant or animal to another or... Read More
Atomic weight
Atomic weight (Science: chemistry) The average weight of an atom of an element, i.e. The total mass of protons and neutrons... Read More
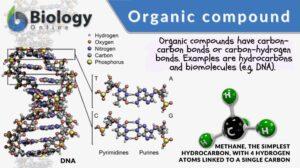
Organic compound
Organic Compound Definition An organic compound is a compound that, in general, contains carbon covalently bound to other... Read More
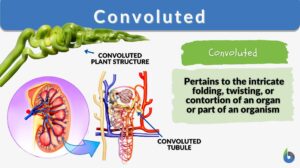
Convoluted
The word convoluted is often used to describe different things, especially structures or components, that have overlapped.... Read More
Active site
Definition noun, plural: active sites The specific region of an enzyme where a substrate binds and catalysis takes place or... Read More
Inorganic compound
Inorganic Compound Definition An inorganic compound is a chemical compound lacking both carbon-carbon (C-C) and... Read More
Electropositive
Electropositive 1. (Science: chemistry, physics) Of such a nature relatively to some other associated body or bodies, as to... Read More
Xylem vessel
Definition noun, plural: xylem vessels (botany) One of the tracheary elements of xylem that is characterized by being made... Read More
Biotechnology
Biotechnology Definition Biotechnology is a technology that uses biological systems or living organisms for a particular... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Atomic mass
Atomic mass (Science: chemistry, physics) The mass of an atom relative to other atoms. The present-day basis of the scale of... Read More