Search Results for: fermentation
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
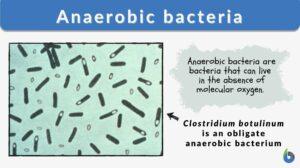
Anaerobic bacteria
Bacteria are classified according to the need for oxygen to survive and grow. For example, aerobic bacteria are bacteria... Read More
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
Alcoholic Fermentation
Alcoholic Fermentation is a type of cellular Respiration which does not require oxygen (anaerobic respiration), and involves... Read More
Oxidation-fermentation test
Definition noun A test used to identify bacteria by the way they metabolize a carbohydrate substrate (e.g. glucose) whether... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Aerotolerant
Aerotolerant Definition The term "aerotolerant" pertains to an organism that does not require oxygen for growth but can... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Industrial Microbiology
Definition noun Related to environmental, social and economic importance that are engaged in the utilization of... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
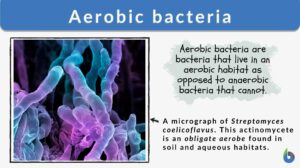
Aerobic bacteria
Aerobic Bacteria Definition What does aerobic mean in biology? As the name suggests, 'aerobe' in biology means organisms... Read More
Galacto-oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: galacto-oligosaccharides ga·lac·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride An oligosaccharide made up of... Read More
Lactic acid
Definition noun (1) A colorless or yellowish, syrupy, water-soluble liquid, which is a byproduct of anaerobic glucose... Read More
Pasteur effect
Definition noun The inhibiting effect of oxygen on the fermentation process. Supplement The effect was discovered in 1857 by... Read More
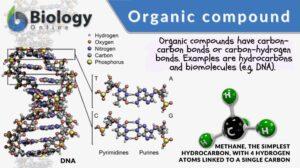
Organic compound
Organic Compound Definition An organic compound is a compound that, in general, contains carbon covalently bound to other... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Clostridium tetani
Definition noun An obligate anaerobic rod shaped and gram-positive bacterium which appears to looks like a drumstick that is... Read More
Lactobacillus casei
Definition noun A non-pathogenic and harmless bacterium recognized widely as probiotics that controls growth of various... Read More
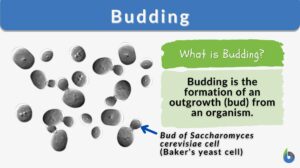
Active dry yeast
Definition noun A form of dry yeast in which the yeasts are not killed but made dormant through dehydration, and return to... Read More
Pseudovitamin b12
pseudovitamin B12 (Science: biochemistry) Cobamide cyanide phosphate, 3'-ester with 7-alpha-d-ribofuranosyladenine, inner... Read More
Gluconeogenesis
Definition noun The metabolic process in which glucose is formed from non-carbohydrate precursors Supplement Glucose is an... Read More
Guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Metabolic rate
Definition noun (1) The rate of metabolism, i.e. the amount of energy used in a certain period. (2) closely approximated* by... Read More
Reducing sugar
Reducing Sugar Definition What is reducing sugar? The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively... Read More
Obligate anaerobe
Definition noun An anaerobe that does not require oxygen and lives only in anaerobic environment. Supplement Exposure to... Read More
Staphylococcus aureus
Definition Noun A gram-positive spherical and facultative bacterium arranged in cluster involved as pathogens of several... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More