Search Results for: glycoprotein
Glycoprotein
Definition noun, plural: glycoproteins Any of the conjugated proteins, characterized by having one or more... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Glycosylation
Definition noun A biochemical process where a glycan attaches to a protein, a lipid, or other organic molecule, especially... Read More
Galactosamine
Definition noun, plural: galactosamines A hexosamine, where galactose contains an amine (-NH2) instead of a hydroxyl (–OH)... Read More
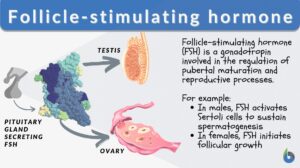
Follicle-stimulating hormone
Follicle Stimulating Hormone Definition In the pituitary gland of the brain, gonadotropic hormones are released.... Read More
Erythropoietin
Definition noun, plural: erythropoietins A glycoprotein hormone that regulates the production of red blood cells in the bone... Read More
Thrombopoietin
Definition noun, plural: thrombopoietins A glycoprotein hormone produced by liver and kidney associated with the production... Read More
Amino sugar
Definition noun, plural: amino sugars A sugar molecule the nonglycosidic hydroxyl (–OH) group is replaced by an amine... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. In fact, there are countless species of single-celled organisms,... Read More
Fibrinogen
Definition noun, plural: fibrinogens A soluble rod-shaped plasma glycoprotein (340 kd, 46 nm long) consisting of six peptide... Read More
Glycoconjugate
Definition noun, plural: glycoconjugates A carbohydrate chemically linked to another compound, e.g. lipid or... Read More
Middle lamella
Definition noun plural: middle lamellae ˈmɪdəl ləˈmɛl.ə A pectin-rich intercellular material that glues the... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Elastic fiber
Definition noun, plural: elastic fibers A type of connective tissue fiber that is made up, primarily, of elastin, and found... Read More
Glycosidase
Definition noun, plural: glycosidases (biochemistry) An enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of a... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Nuclease S1
Definition noun An endonuclease enzyme capable of degrading single-stranded DNA and RNA Supplement The nuclease S1 is a... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Luteinizing hormone
Definition noun, plural: luteinizing hormones A gonadotropin released by the gonadotropes of the anterior pituitary, and,... Read More
Secondary cell wall
Definition noun plural: secondary cell walls ˈsɛkənˌdɛɹi sɛl wɔːl The layer of the plant cell wall that forms... Read More
Glycolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycolipids A carbohydrate, usually an oligosaccharide, that is covalently linked to a lipid... Read More
Immunoglobulin A
Definition noun An immunoglobulin (antibody) that is characterized by its α-heavy chain, and its prevalence in mucous... Read More
Bacteriolysin
Definition noun, plural: bacteriolysins (1) A specific antibody that combines with bacterial cells (antigens) and, in the... Read More
Thyrotroph
Definition noun, plural: thyrotrophs The cell in the anterior pituitary that particularly releases thyroid-stimulating... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Role of Golgi Apparatus & Endoplasmic Reticulum in Protein Synthesis
Continued from the previous tutorial that introduces protein synthesis... mRNA and tRNA mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters... Read More
Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.The inheritance patterns seen in Mendel's monohybrid and dihybrid crosses... Read More
Parietal cell
Definition noun, plural: parietal cells Any of the epithelial cells in the gastric gland responsible for the secretion of... Read More
Abo blood group
Abo blood group (Science: haematology) The major human blood type system which describes the oligosaccharide glycoprotein... Read More