Search Results for: homologous chromosome
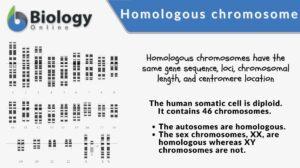
Homologous chromosome
A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Recombination DNA repair
Recombination DNA Repair Definition Recombination DNA repair is a biological reparative process in response to DNA damage... Read More
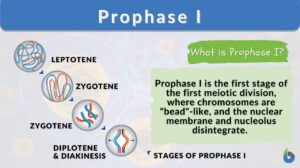
Prophase I
Organisms all use mitosis to create more cells in the body. Meiosis, a similar process, is used in some organisms to undergo... Read More
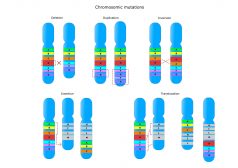
Chromosome Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.By nature, the genetic information from both parents is expected to be seen... Read More
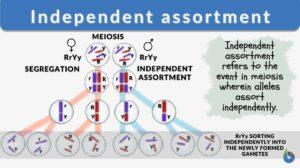
Independent Assortment
Independent Assortment Definition Independent assortment refers to the alleles or genes that sort into the newly formed... Read More
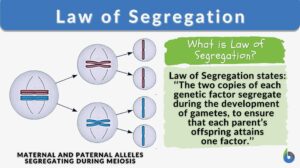
Law of Segregation
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance The father of genetics, Gregor Mendel, reported his findings in 1860 that initially were... Read More
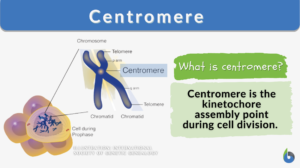
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
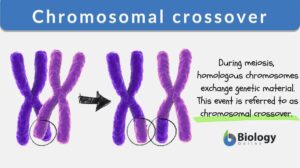
Chromosomal crossover
Chromosomal Crossover Definition noun A process occurring during meiosis wherein homologous chromosomes pair up and... Read More
Meiosis and Alternation of Generations
Review of Mitosis: Cell Cycle The cell cycle contains the process in which cells are either dividing or in between... Read More
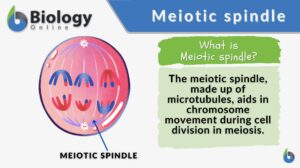
Meiotic spindle
Meiotic Spindle Definition The meiotic spindle refers to the spindle apparatus that forms during meiosis in contrast to... Read More
Chromosomes X and Y and Sex Determination
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.In humans, the normal chromosome complement is 46, consisting of 22 pairs of... Read More
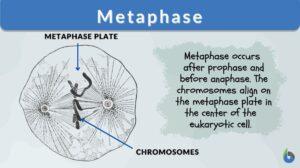
Metaphase I
Definition noun The second stage in the first meiotic division after prophase I, and highlights the alignment of paired... Read More
Heterozygote
Definition noun, plural: heterozygotes A nucleus, cell or organism possessing two different alleles for a particular... Read More
Anaphase I
Definition noun The third stage in the first meiotic division after prophase I, and highlights the separation of paired... Read More
Independent Assortment and Crossing Over
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.The previous tutorial investigates the process of meiosis, where... Read More
Non-sister chromatid
Definition noun, plural: non-sister chromatids Either of the two chromatids of any of the paired (homologous)... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
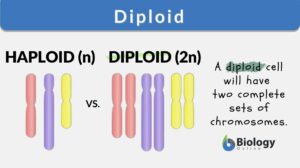
Allotetraploid
Allotetraploid Definition An allotetraploid is an organism with four sets of chromosomes (4n). This is in contrast to the... Read More