Search Results for: host cell
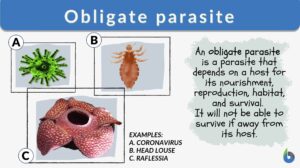
Obligate parasite
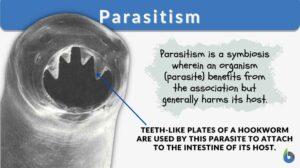
Parasitism is a form of symbiosis that occurs between a parasite and its host. The parasite is the organism that generally... Read More
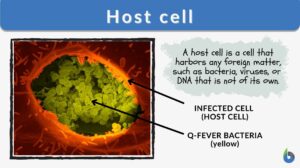
Reservoir host
Reservoir Host Definition A reservoir host is a host that harbors the pathogen and serves as a source of the infective... Read More
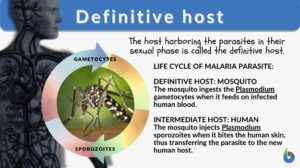
Definitive host
Different Biological Relationships The biological world is interconnected whether we notice it or not. All the life forms... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Parasitism
Organisms depend on different sources of food to survive. Larger organisms like plants make their own food (autotrophs) and... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
Biological Viruses
The prime directive of all organisms is to reproduce and survive and this also applies to viruses. Apparently, viruses are... Read More
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
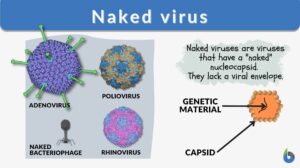
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
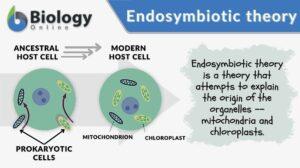
Endosymbiotic theory
A eukaryotic cell is distinct from a prokaryotic cell by the presence of membrane-bound cellular structures called... Read More
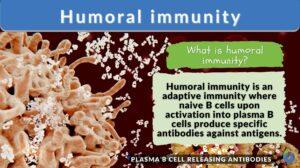
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More
Cytotoxic T cell
Definition noun, plural: cytotoxic T cells A T cell responsible for inducing death to target cells (e.g. infected somatic... Read More
Density dependent factor
Density-dependent factors are the limiting factors of an ecosystem that regulate population growth in a density-dependent... Read More
Endoparasite
Definition noun, plural: endoparasites (parasitology) A parasite that lives within the body of the... Read More
Susceptible
Resistance, vulnerability, sensitivity, tolerance, and susceptibility are some highly important terminologies across the... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Lytic cycle
Definition noun One of the two cycles of viral reproduction (the other being the lysogenic cycle), which is usually... Read More