Search Results for: intracellular
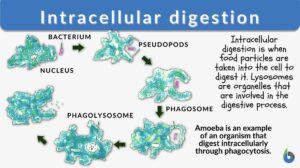
Intracellular digestion
Intracellular Digestion Definition What is intracellular digestion? ‘Intra’ means "inside" and ‘cellular’ pertains... Read More
Intracellular fluid
Definition noun The body fluid within the cell composed mainly of water dissolved ions, and other molecules Supplement The... Read More
Intracellular
Definition adjective Occurring or being (situated) inside a cell or cells. Supplement For example, intracellular fluid... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Microtubule
Microtubule Definition noun plural: microtubules mi·cro·tu·bule, mī'krō-tū'byūlA cytoplasmic tubule made up of... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Microfilament
Definition noun plural: microfilaments mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī'krō-fil'ă-mĕnts A thin, helical, single-stranded... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Intermediate filaments
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. WrightDepartment of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
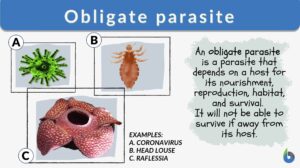
Obligate parasite
Parasitism is a form of symbiosis that occurs between a parasite and its host. The parasite is the organism that generally... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
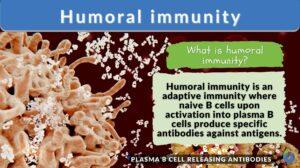
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
Endoparasite
Definition noun, plural: endoparasites (parasitology) A parasite that lives within the body of the... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of guanosine monophosphate (chemical... Read More
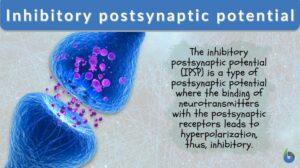
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
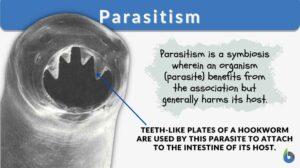
Parasitism
Organisms depend on different sources of food to survive. Larger organisms like plants make their own food (autotrophs) and... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of adenosine monophosphate that... Read More
Adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More