Search Results for: metabolic rate
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
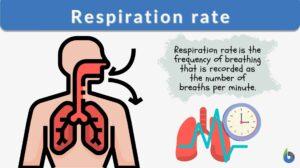
Respiration rate
Respiration Rate Definition Respiration rate is a vital life process that expresses the breathing rate in an organism... Read More
Metabolic rate
Definition noun (1) The rate of metabolism, i.e. the amount of energy used in a certain period. (2) closely approximated* by... Read More
Basal metabolic rate
Basal metabolic rate is the amount of enrgy required to sustain only vital organs when one is at rest (Science:... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo MinnsSubmitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009.Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and BehaviorHaving discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Environmental resistance
Environmental Resistance Definition Environmental resistance is such a process in which certain different elements or... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
Net primary productivity
In order to keep the biosphere running, different organisms play different roles and functions. Some help in oxygen... Read More
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Animal Growth Hormones
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.As mentioned in the previous tutorial, hormones are produced in... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Sleep and Dreams – Neurology
The Falling Asleep Process During the day when we are awake, our body and brain are working tirelessly to operate our body,... Read More
Infradian rhythm
What is the Infradian Rhythm? An infradian rhythm is a type of biological rhythm that lasts longer than 24 hours, with a... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Addressing the Unmet Medical Need for Safe and Effective Weight Loss Therapies
Perspective Addressing the Unmet Medical Need for Safe and Effective Weight Loss Therapies Cynthia M. Arbeeny Address... Read More
Great Oxygenation Event
Great Oxygenation Event Definition The Great Oxygenation Event is defined as the surge of dioxygen (O2) levels in the... Read More
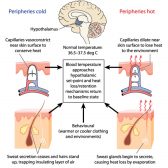
Temperature Regulation in Animals
Control of Temperature in Homeotherms Animals capable of temperature regulation within a given range are deemed homeotherms... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
A Balanced Diet – Minerals and Proteins
Minerals Various minerals in the Earth's crust are required for a healthy balanced diet. These inorganic compounds have... Read More
Effect of Chemicals on Growth & Development in Organisms
Plants Plants require a large number of elements to function properly, mainly carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, essentially... Read More