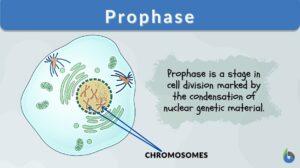
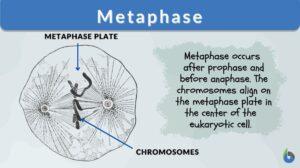
Search Results for: nuclear division
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
Nuclear division
Definition noun The process by which a nucleus divides, resulting in the segregation of the genome to opposite poles of a... Read More
Nuclear lamina
Definition noun plural: nuclear laminae or nuclear laminas nu·cle·ar lam·i·na, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈlæm.ɪ.nə (cell... Read More
Nuclear envelope
Definition noun plural: nuclear envelopes nu·cle·ar en·ve·lope, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈɛn.və.ləʊp The two layered membrane... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Nuclear matrix
Definition noun plural: nuclear matrices (cell biology) A 3-dimensional filamentous protein network that extends... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
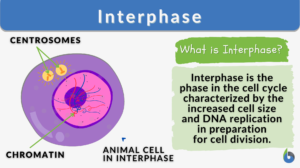
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
Perinuclear space
Definition noun plural: perinuclear spaces per·i·nu·cle·ar space The space or gap between the inner and outer... Read More
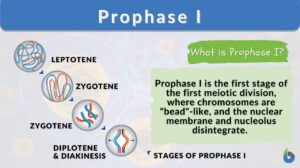
Prophase I
Organisms all use mitosis to create more cells in the body. Meiosis, a similar process, is used in some organisms to undergo... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Meiosis and Alternation of Generations
Review of Mitosis: Cell Cycle The cell cycle contains the process in which cells are either dividing or in between... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
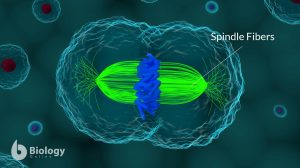
Spindle fiber
Definition noun, plural: spindle fibers Any of a network of filaments that collectively form a mitotic spindle (in... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Interkinesis
Definition noun Interphase II, i.e. a short resting period occurring between meiosis I and meiosis II Supplement Meiosis is... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
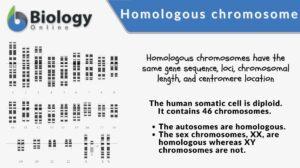
Homologous chromosome
A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and... Read More
Meiosis II
Definition The second of the two consecutive divisions of the nucleus of eukaryotic cell during meiosis, and composed of the... Read More
Karyostenosis
Karyostenosis (Science: biology) direct cell division (in which there is first a simple division of the nucleus, without any... Read More
Diakinesis
Definition noun The final stage of prophase I of meiosis I in which the chromosomes condense, the nucleolus fragments and... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
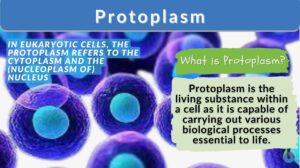
Protoplasm
Protoplasm Definition The protoplasm is regarded as "the living material or the living content of a cell". It is fluid... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More