Search Results for: producer
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
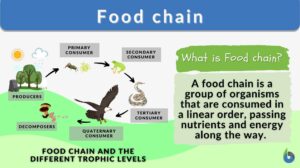
Food chain
Everything is a cycle in life. The way organisms consume their food also follows a cycle. This is usually described as the... Read More
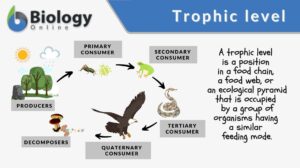
Trophic level
In ecology, a trophic level pertains to a position in a food chain or ecological pyramid occupied by a group of organisms... Read More
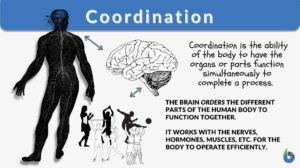
Coordination
Coordination Definition When a person hears the word coordination, they think of order, organization, or even managing... Read More
Heterotroph
Heterotroph Definition What is a heterotroph? Does a heterotroph make its own food? In biology and ecology, a heterotroph... Read More
Net primary productivity
In order to keep the biosphere running, different organisms play different roles and functions. Some help in oxygen... Read More
Bacterioplankton
Definition noun The bacterial component of plankton of aquatic ecosystems Supplement Plankton pertain to the small organisms... Read More