Search Results for: reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species
Definition noun Chemically reactive molecules and ions of oxygen with an unpaired electron Supplement Reactive oxygen... Read More
Aerotolerant
Aerotolerant Definition The term "aerotolerant" pertains to an organism that does not require oxygen for growth but can... Read More
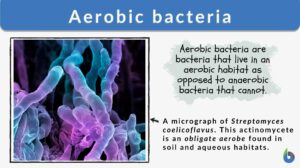
Aerobic bacteria
Aerobic Bacteria Definition What does aerobic mean in biology? As the name suggests, 'aerobe' in biology means organisms... Read More
Obligate aerobe
Before we define obligate aerobes, let us first understand and define aerobic organisms. Aerobic organisms are those that... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Phagolysosome
Definition noun plural: phagolysosomes (cell biology) A cytoplasmic body that forms from the fusion of phagosome and... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Oxidative phosphorylation
Definition noun A metabolic pathway that generates ATP from ADP through phosphorylation that derives the energy from the... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
Senescence
Senescence Definition Senescence is defined as biological aging. In cell biology, it refers to the cell wherein it is no... Read More
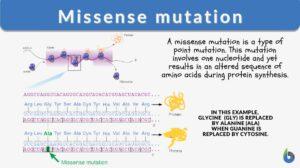
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More