Search Results for: regeneration
Regeneration in humans – Finding the gene switch
Regeneration in humans is much more limited compared in other animals. Say for instance when one lost a limb, much as well... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Aberrant regeneration
Aberrant regeneration Misdirected regrowth of nerve fibres seen for example, after oculomotor nerve injury. Synonym:... Read More
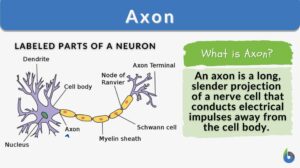
Regeneration
regeneration The natural renewal of a structure, as of a lost tissue or part. Origin: L. Generare = to produce, bring to... Read More
Fragmentation
Fragmentation Definition What is fragmentation? In general, fragmentation refers to the state or the process of breaking... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Physical Development in Humans
The Newly Born Child Depending on the nutrients available to the child within pregnancy and the genetic makeup of the... Read More
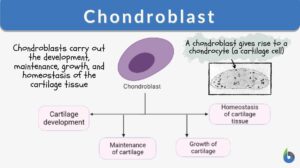
Chondroblast
There are two forms of cells in cartilage: chondroblasts and chondrocytes. The chondroblasts are cells that secrete the... Read More
Reproduction
Reproduction Definition Reproduction is a biological phenomenon of producing offspring/s. i.e. more of its kind. Depending... Read More
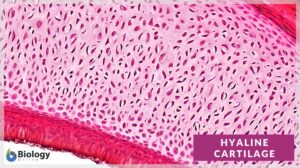
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Before we define hyaline cartilage, let us understand what cartilage is. What is cartilage? Is... Read More
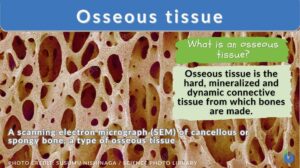
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
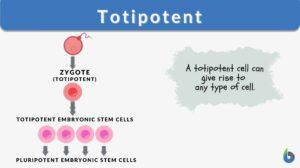
Totipotent
Totipotent Definition What is totipotent? In general terms, totipotency is defined as the ability of a single cell to... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Pangenesis
Definition noun A hypothetical mechanism for heredity proposed by Charles Darwin in which it holds that gemmules are shed... Read More
Myogenesis
Definition noun (embryology) The formation of muscle tissues through the differentiation of progenitor cells myoblasts... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Olfactory nerve
Definition noun, plural: olfactory nerves The cranial nerve comprised of sensory nerve fibers that carry impulses for the... Read More
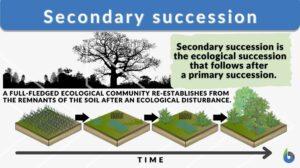
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
Eponychium
The eponychium is the layer present underneath the proximal nail fold that produces cuticles on the nail.... Read More
Recalcitrant
Several words of the English language find wide usage in subjects as diverse as literature, science, social science,... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
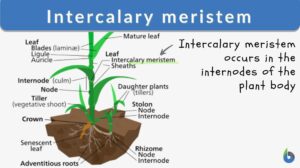
Intercalary meristem
The basic structural framework of plants is composed of different types of tissues. Based upon the capacity to divide, the... Read More