Search Results for: saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
saccharomyces cerevisiae (Science: fungus) A species of yeast which is an important model organism for biological study,... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Reproduction
Reproduction Definition Reproduction is a biological phenomenon of producing offspring/s. i.e. more of its kind. Depending... Read More
Nuclear body
Definition noun plural: nuclear bodies nu·cle·ar bod‧y, ˈnjuː.kli.ər ˈbɒdi Any of the prominent non-membraned,... Read More
Nuclear pore complex
Definition noun plural: nuclear pore complexes ˈnu kli ər, pɔː ˈkɒmplɛks A complex of nucleoporins resulting in the... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Asexual reproduction
Asexual Reproduction Definition What is asexual reproduction? Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
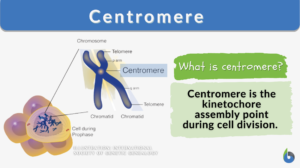
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Crabtree effect
Definition noun The aerobic production of ATP, inhibition of cell respiration, and production of ethanol as coupled events... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More