Search Results for: somatic cells
Somatic cells
Definition noun, singular: somatic cell The word “somatic” is derived from the Greek word soma, meaning “body”.... Read More
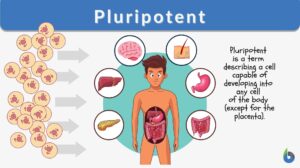
Pluripotent
Pluripotent Definition What is pluripotent? In biology, the term "pluripotent" means capable of developing into... Read More
First time! Human blood cell turned into a young sex cell
In essence, our body consists of two major types of cells – one group involved directly in reproducing sexually (called... Read More
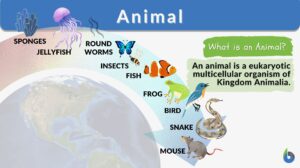
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
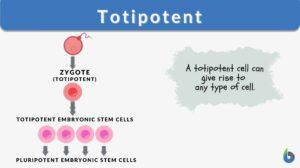
Totipotent
Totipotent Definition What is totipotent? In general terms, totipotency is defined as the ability of a single cell to... Read More
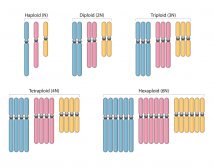
Polyploidy
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.Polyploidy Polyploidy is defined as the state of being polyploid, which... Read More
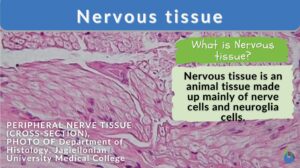
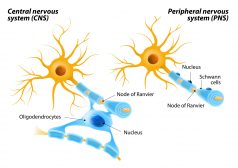
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
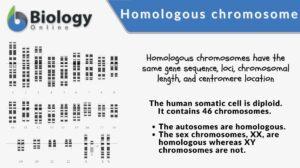
Homologous chromosome
A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and... Read More
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction involving the fusion of haploid female gamete (egg cell) and haploid male... Read More
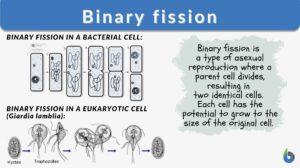
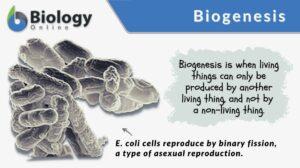
Binary fission
Binary Fission Definition What is binary fission? In biology, binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where a... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Biogenesis
Biogenesis Definition Biogenesis refers to the idea or the process whereby a living thing comes from another living thing,... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
The Central Nervous System
Myelin Sheath Myelin is a substance that forms the myelin sheath associated with nerve cells. This sheath is a layer of... Read More
Cytotoxic T cell
Definition noun, plural: cytotoxic T cells A T cell responsible for inducing death to target cells (e.g. infected somatic... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More