Search Results for: surface water
Surface water
Definition noun (ecology) Water that is above the substrate or soil surface such as streams, bays, lakes, rivers, seas,... Read More
Running Water Freshwater Communities
Running water freshwater communities are also known as lotic communities, lotic meaning running water. Lotic communities are... Read More
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic Definition The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Plant Water Regulation
A plant requires water as an essential ingredient of photolysis, the photochemical stage of photosynthesis where water is... Read More
Macrophytes
Introduction Examples of Macrophytes. (Source: Canada's AquaticEnvironments) ... Read More
Freshwater Communities & Lentic Waters
Lentic (still water) communities can vary greatly in appearance, anything from a small temporary puddle to a large lake is... Read More
The Water Cycle
The water cycle (sometimes referred to as the hydrological cycle) is the continuous transfer of water from air, sea land and... Read More
Environment
Environment Definition What does environment mean? If you mean physical environment, then it is defined as the surrounding... Read More
Animal Water Regulation
Homeostatic control, a set environment, and how evolution and natural selection drives a species to adapt to its environment... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Abiotic Factors – Water Conditions
Evidently, the light and heat from the sun play an important role in providing suitable conditions. However, the water... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Still Water Animals
Through millions of years of evolution, animals living in an aquatic environment have diversified to occupy the ecological... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Abiotic factor
An abiotic factor is a non-living element of the environment that influences the way organisms and ecosystems function. Some... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma.Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Still Freshwater & Plants
Plants in the freshwater community provide a means of food for herbivores and harness new energy into the community as a... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
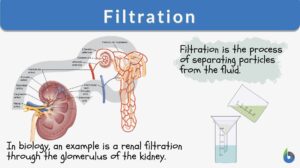
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More