Search Results for: systole
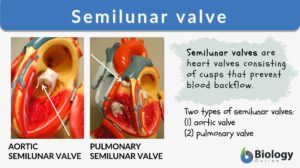
Semilunar valve
The human heart structure consists of heart chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles) that differ functionally from each other.... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Pulmonary valve
Definition noun, plural: pulmonary valves (anatomy, cardiology) The semilunar valve that lies between the right ventricle... Read More
Blood pressure
Blood pressure (Science: cardiology, physiology) The force that the circulating blood exerts on the walls of the... Read More
Heart valve
Definition noun, plural: heart valves (anatomy) Any of the valves of the heart that prevents the back flow of blood through... Read More
Heart sounds
Heart sounds The sounds heard over the cardiac region produced by the functioning of the heart. There are four distinct... Read More
Contractile vacuole
Definition noun, plural: contractile vacuoles (cell biology) A specialized vacuole of eukaryote cells, especially protozoa,... Read More
Dicrotic notch
Definition noun 1. The brief rise or upstroke in a pulse tracing that occurs before the dicrotic wave, and represents a... Read More