Search Results for: transition
Demographic transition
The demographic transition model is a theoretical framework that explains the historical shift in population dynamics as a... Read More
Transition
Definition noun, plural: transitions (genetics) A small-scale mutation characterized by the replacement of a purine by... Read More
Health transition
Health transition Demographic and epidemiologic changes that have occurred in the last five decades in many developing... Read More
Transition mutation
transition mutation A point mutation involving substitution of one base-pair for another, i.e., replacement of one purine... Read More
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Geological Periods
Precambrian Times (Most Ancient) All time before life existed, Earth was still a volatile environment, though the origins... Read More
Activation energy
Definition noun The amount of energy (in joules) needed to convert all the molecules in one mole of a reacting substance... Read More
Phosphodiester bond
Phosphodiester Bond Definition Phosphodiester bonds are the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid present in the life... Read More
Transversion
Definition noun, plural: transversions (genetics) A small-scale mutation characterized by the replacement of a purine by... Read More
Great Oxygenation Event
Great Oxygenation Event Definition The Great Oxygenation Event is defined as the surge of dioxygen (O2) levels in the... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
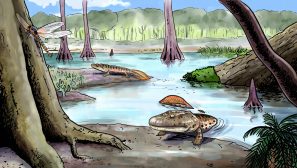
Amphibians & Early Reptiles
Amphibia Definition (Science: zoology) Amphibia is one of the classes of vertebrates.The amphibia are distinguished by... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
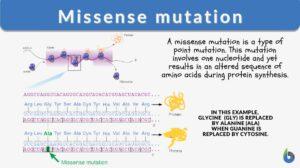
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
Substitution mutation
Definition noun, plural: substitution mutations (genetics) A small-scale mutation characterized by a substitution of one or... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Mammalian Ancestors
Humans are mammals, the most successful taxonomic class of organisms to colonize the Earth. The word mammal derives from the... Read More
Arthropods
There are over two million species of arthropods, who initially arrived on Earth in the middle of the Cambrian period.... Read More
Primitive Animals
Incorrect taxonomic classifications deemed organisms to be either animals or plants, in the Plantae or Animalia kingdoms... Read More
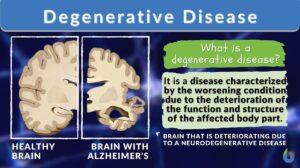
Degenerative disease
Degenerative Disease Definition A degenerative disease is defined as a disease characterized by the worsening condition due... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
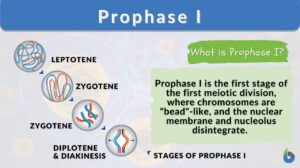
Prophase I
Organisms all use mitosis to create more cells in the body. Meiosis, a similar process, is used in some organisms to undergo... Read More
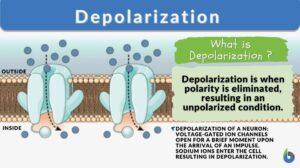
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
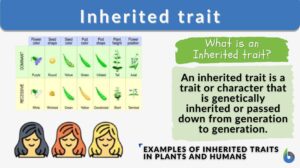
Inherited traits
What are Inherited Traits? The characteristics or traits that are passed from parents to offspring are known as inherited... Read More