Search Results for: yield
Crop yield
Definition noun The amount of plant crop (such as cereal, grain or legume) harvested per unit area for a given... Read More
Milk yields affected by music tempo
Dairy cows produce more milk when listening to REM's 'Everybody Hurts' or Beethoven's 'Pastoral Symphony' than when... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Amyloglucosidase
Definition noun A form of amylase that cleaves the last alpha-1,4-glycosidic linkages at the nonreducing end of amylase and... Read More
Gamma-amylase
'Definition noun, plural: gamma-amylases A form of amylase that cleaves the last alpha-1,4-glycosidic linkages at the... Read More
Genetic variability
Genetic Variability Definition Genetic variability refers to the tendency of individual genetic characteristics in a... Read More
Obligate anaerobe
Definition noun An anaerobe that does not require oxygen and lives only in anaerobic environment. Supplement Exposure to... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life ... Read More
Testosterone
Definition noun, plural: testosterones A steroid hormone with a chemical formula of C19H28O2, and is regarded as the primary... Read More
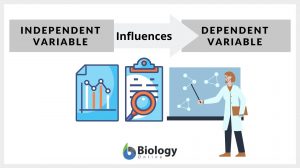
Independent variable
Independent Variable Definition To define an independent variable, let us first understand what a variable is. The word... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
Gluconeogenesis
Definition noun The metabolic process in which glucose is formed from non-carbohydrate precursors Supplement Glucose is an... Read More
Pyrimidine
Definition noun plural: pyrimidines py·rim·i·dine, py·rim·i·dine A heterocyclic aromatic compound that presents as... Read More
Oxidative phosphorylation
Definition noun A metabolic pathway that generates ATP from ADP through phosphorylation that derives the energy from the... Read More
Cytidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is composed of cytidine (a cytosine... Read More
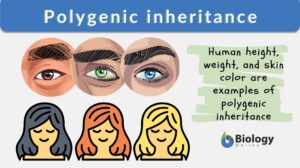
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
CRISPR DIY – biohacking genes at home
Have you ever thought of changing yourself for the better -- genetically-speaking? Lately, CRISPR company has been selling a... Read More
First time! Human blood cell turned into a young sex cell
In essence, our body consists of two major types of cells – one group involved directly in reproducing sexually (called... Read More
Selective Breeding
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, PhDThousands of years before Darwin proposed evolution by natural selection and... Read More
Effect of Chemicals on Growth & Development in Organisms
Plants Plants require a large number of elements to function properly, mainly carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, essentially... Read More
Population Regulation in an Ecosystem
Darwin focused some of this work in regards to the population size of a species, and what factors may affect them. He... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma.Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Sphingolipid
Definition noun plural: sphingolipids sphin·go·lip·id A type of lipid with a sphingoid base (e.g. sphingosine and... Read More
Deoxyribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: deoxyribonucleotides de·ox·y·ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, diˌɒk... Read More
Thymidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and three... Read More
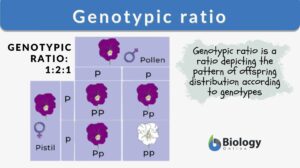
Genotypic ratio
Genotypic Ratio Definition To understand 'Genotypic ratio', let us first understand the terms: 'Genotype' and 'Phenotype'.... Read More
Thymidine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and two... Read More