Consciousness and Behavior

States of consciousness is defined by behavior and electrical pattern of brain activity
Table of Contents
States of Consciousness
Defined either by (1) behavior – ranging from attentive and alert to coma and (2) electrical pattern of brain activity, recorded as an electroencephalogram (EEG).
Electroencephalogram
The electric potential difference between two points on the scalp. The amplitude indicates a degree of synchronous activity and frequency indicates responsiveness (low frequency = sleep to high frequency = alert).
Wakeful State
The high frequency, low amplitude wave pattern of an awake relaxed adult is called the alpha rhythm. As people become more attentive, the wave pattern becomes low amplitude, high-frequency oscillations called the beta rhythm. This transformation is called EEG arousal.
Sleep
Has 2 phases:
- The longer NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep, which shows a high amplitude-low frequency wage pattern. Growth hormone and gonadotropic hormones are released. Blood pressure, heart and respiratory rates decrease.
- REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, which shows a wave pattern similar to the awake state – the reason it is also called paradoxical sleep. Skeletal muscle tension is decreased during this phase except that in the eye and the respiratory muscles. Blood pressure, heart and respiratory rates increase.
Neural Substrates of States of Consciousness
Periods of sleep and wakefulness show a circadian or daily rhythm, the clock timing of which depends on the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Aminergic neurons that release norepinephrine or serotonin are dominant during wakefulness while cholinergic neurons are dominant during REM sleep. NREM sleep is intermediate to these two states.
Coma and Brain Death
Coma is a severe decrease in mental function due to structural, physiological or metabolic impairment of the brain. A person in a coma is characterized by a sustained loss of capacity for arousal even in response to vigorous stimulation. There is no outward behavioral expression of any mental function and sleep-wake cycles disappear. Brain death is an irreversible coma without drug intoxication. There should not be any functioning neural tissue above the spinal cord.
Conscious Experiences
Sensory awareness and awareness about mental representations
Directed Attention
Avoidance of irrelevant stimuli and focusing on relevant stimuli is called directed attention. Preattentive processing of information directs attention toward meaningful stimuli before we focus on them. Focusing is possible without making any behavioral response. If it is followed by an orientation toward the stimulus source, it is called the orienting response. If the behavioral response to the stimulus progressively decreases as it is found to be irrelevant, it is called habituation.
Neural Mechanisms for Directed Attention
Directing attention to an object involves 3 neurological processes:
- Disengaging attention from present focus,
- Moving attention to new focus
- Engaging attention to new focus Brainstem plays an important role in the orienting response. The locus ceruleus, a-nucleus in the brainstem, directs the information to particular areas in the brain. The cerebral cortex is involved in the perception of the stimulus.
Motivation and Emotion
Motivation
Motivation is responsible for goal-directed behavior. Motivation leads to hormonal, autonomic or behavioral responses. Behavior related directly to homeostasis is called primary motivated behavior. If the relation between the behavior and the goal is indirect, it is secondary motivated behavior and this is influenced by factors called incentives such as habit, learning, etc. Motivations may be shaped by rewards (positive reinforcers) or punishments (negative reinforcers). The mesolimbic dopamine pathway is involved in the motivation process.
Emotion
An individual’s assessment of the environment and their disposition to it. Amygdala, a cluster of nuclei on the temporal lobe, is central to emotional states.
Altered States of Consciousness
Schizophrenia
Information is not properly regulated in the brain. Motor control is abnormal. Dopamine pathways are overactive.
Mood disorders: depressions and bipolar disorders
The mood is sustained inner emotion that affects the person’s perception of the world. Depressive disorders are indicated by loss of energy, interest, and anxiety. Bipolar disorders are swings between depression and mania -an abnormally elated mood. It can be treated by electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) in which pulses of electric current are used to activate a large number of neurons and alter neurotransmitter function to down-regulate some postsynaptic receptors.
Psychoactive substances, dependence, and tolerance
Psychoactive substances exert their actions by altering neurotransmitter-receptor interactions. Psychological dependence is craving for a substance and an inability to stop. Physical dependence requires one to take the substance to avoid withdrawal physiological symptoms occurring with the cessation of substance use. Tolerance to a substance occurs when increasing doses of a substance are required to achieve the desired effect. Cross-tolerance is the development of tolerance to one substance due to the use of another.
Learning and Memory
Learning is the acquisition and storage of information as a consequence of experience. Measured y an increase in the likelihood of a particular behavior in response to a stimulus. Rewards and punishment influence learning.
Memory
Permanent stored form of learned information. Processes that mediate between learning and memory are called memory encoding. Two types: (1) Declarative memory is knowledge of one’s past experience of the world. The limbic system is important for this type of memory. (2) Non-declarative memory is memory for the performance of skilled behaviors. The sensorimotor cortex, basal ganglia, and cerebellum are important for this type of memory.
Working memory
Working memory is the primary or short-term memory that registers and retains information for a very short time. It makes possible a temporary impression of one’s present environment in a readily accessible form. Focusing attention is important for memory-based skills.
Cerebral Dominance and Language
In the majority of the population, the left cerebral hemisphere is specialized to produce language. Distinct areas are specialized for different language skills. During development, assignment of language functions can take place in either hemisphere but it progressively shifts to the left. Although language skills emerge spontaneously in all children, they must be exposed to language during a critical period. Verbal memory is associated with the left hemisphere and nonverbal memory is associated with the right.
You will also like...

Human Reproduction
Humans are capable of only one mode of reproduction, i.e. sexual reproduction. Haploid sex cells (gametes) are produced ..

Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
The human body is capable of regulating growth and energy balance through various feedback mechanisms. Get to know the e..
Primitive Animals
Life, as we know it today, is presumed to have started in the sea and many of them were likely eukaryotic animal-like or..

Population Regulation in an Ecosystem
With regard to the population size of a species and what factors may affect them, two factors have been defined. They ar..

Developmental Biology
Developmental biology is a biological science that is primarily concerned with how a living thing grows and attains matu..
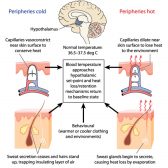
Temperature Regulation in Animals
This tutorial elucidates body temperature regulation. Know the details here to learn how the body sets the body temperat..
