Examples of Natural Selection

Peppered moth (“Biston betularia”) melanic and light form
Table of Contents
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.
Darwin’s Finches
Darwin’s finches are an excellent example of the way in which species’ gene pools have adapted in order for long term survival via their offspring. Darwin’s Finches diagram below illustrates the way the finch has adapted to take advantage of feeding in different ecological niches.
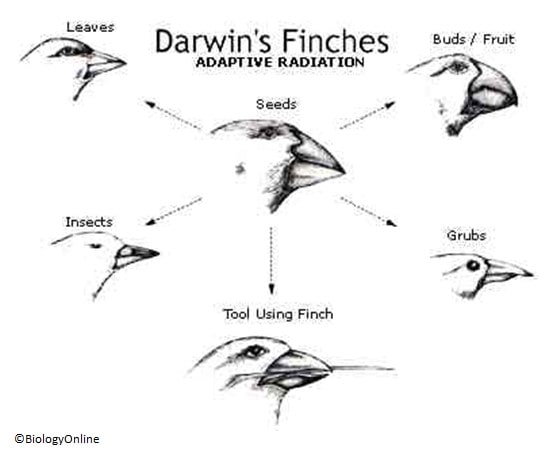
Their beaks have evolved over time to be best suited to their function. For example, the finches who eat grubs have a thin extended beak to poke into holes in the ground and extract the grubs. Finches who eat buds and fruit would be less successful at doing this, while their claw-like beaks can grind down their food and thus give them a selective advantage in circumstances where buds are the only real food source for finches.
Industrial Melanism
Polymorphism pertains to the existence of two distinctly different groups of species that still belong to the same species. Alleles for these organisms over time are governed by the theory of natural selection, and over this time the genetic differences between groups in different environments soon become apparent, as in the case of industrial melanism.
Industrial melanism occurs in a species called the peppered moth, where the occurrence has become of more frequent occurrence since the beginning of the industrial age. The following argument elaborates on the basis of principles involved in natural selection as far as industrial melanism is concerned.
- Pollution, which is more common in today’s world since the industrial age causes a change in the environment, particularly in the 1800’s when soot would collect on the sides of buildings from chimneys and industries and make them a darker color.
- The resultant effect was that the peppered moth, which had a light appearance was more visible against the darker backgrounds of sooty buildings.
- This meant that predators of the peppered moth could find them more easily as they are more visible against a dark background.
- Due to mutations, a new strain of peppered moth came to existence, where their phenotype was darker than that of the white peppered moth.
- This meant that these new, darker peppered moths were once again harder to track down by their prey in environments where industry has taken its toll.
- In this instance, natural selection would favor the darker moths in polluted environments and the whiter moths in the lesser polluted environments due to their ability to merge in with their environmental colors and lessen the chances of them being prone to a predator.
Sickle Cell Trait
Consider this argument of natural selection in the case of sickle cell trait, a genetic defect common in Africa.
- Sickle cell trait is a situation that occurs in the presence of a recessive allele coding for hemoglobin, a substance in the blood responsible for the transport of gases like oxygen. The presence of the allele is either partially expressed recessively (sickle cell), or fully expressed by a complete recessive expression which results in full-blown anemia. If this particular allele is dominant, no sickle cell trait is expressed in the phenotype.
- The above occurrences in the case of a recessive allele result in structural defects of red blood cells, severely reducing the organism’s capacity to uptake oxygen.
- It was pointed out that in Africa, there is a high frequency of this mutation, where cases of malaria were high.
- A substantiated link was made noting those who suffer sickle cell trait or anemia were immune to the effects of malaria. See the map below.
- This is yet again natural selection at work. Although sickle cell trait or anemia are not advantageous characteristics on their own, they prove to be advantageous in areas where malaria proves to be a greater threat to preserving the genome (i.e. surviving).
- The incomplete dominance of this genetic expression proves favorable either way.

This is how science has understood natural selection since the first studies involving Darwin. In the 21st century, humans selectively breed species to create hybrid species possessing the best genes of both parents via a process known as selective breeding.
The diversification of several new species from a recent ancestral source, each adapted to utilize or occupy a vacant adaptive zone is referred to as adaptive radiation. Know more about adaptive radiation in the next tutorial.
 | NATURAL SELECTION – TRUE OR FALSE A true-or-false quiz to test the grasp of the underlying concepts and ideas on natural selection. Evaluate your student’s understanding of Charles Darwin’s theory and examples of natural selection. Subjects: Genetics & Evolution |
You will also like...

Roots
This study guide tackles plant roots in greater detail. It delves into the development of plant roots, the root structur..

Plant Tissues
Plant organs are comprised of tissues working together for a common function. The different types of plant tissues are m..

Circulation
The circulatory system is key to the transport of vital biomolecules and nutrients throughout the body. Learn about the ..

Sugar Homeostasis
The blood sugar level is regulated by two hormones. The mechanism behind this type of negative feedback control is descr..
The Conscious & Unconscious Nervous System
This tutorial elaborates on how the nervous system works, particularly at the tissue level of the brain. There are three..

A Balanced Diet – Carbohydrates and Fat
Apart from vitamins, the human body also requires high energy sources such as carbohydrates and fats. If you want an ove..
