DNA Structure & DNA Replication
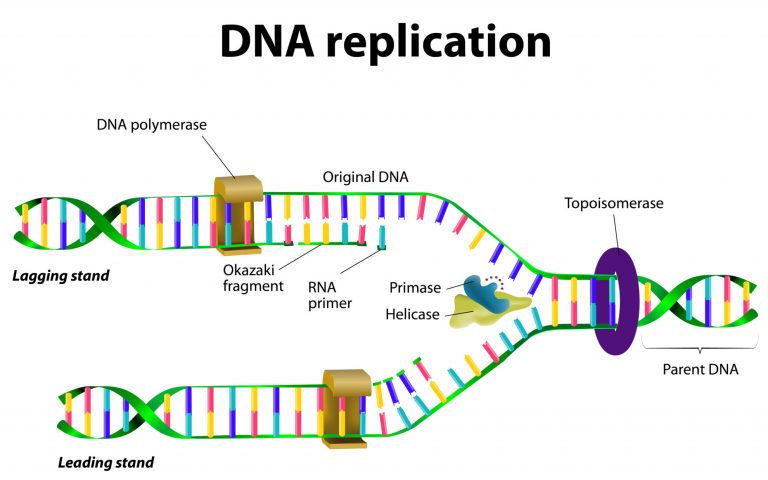
Schematic diagram of DNA replication
Table of Contents
Previous pages in this tutorial have described the basics of a cell, the energy required by these cells and how energy is created in order for the cell to survive (via respiration and photosynthesis).
The structure, type, and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes that are found in the nucleus of a cell. These chromosomes are composed of DNA, the acronym for deoxyribonucleic acid.
This DNA determines all the characteristics of an organism, and contains all the genetic material that makes us who we are. This information is passed on from generation to generation in a species so that the information within them can be passed on for the offspring to harness in their lifetime. The genetics and evolution tutorial goes into more detail about how this genetic information is passed on.
Structure of DNA and Nucleotides
DNA is arranged into a double helix structure where spirals of DNA are intertwined with one another continuously bending in on itself but never getting closer or further away (see diagram to the below right).
The following diagram illustrates a nucleotide, the building blocks of DNA

There are four different types of nucleotide possible in a DNA sequence, adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine (can be replaced with A, C, G and T). There are billions of these nucleotides in our genome, and with all the possible permutations; this is what makes us unique. Nucleotides are situated in adjacent pairs in the double helix nature mentioned. The following rules apply in regards to what nucleotides pair with one another.
- There are four possible types of nucleotide, adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.
- Thymine and adenine can only make up a base pair
- Guanine and cytosine can only make up a base pair
- Therefore, thymine and cytosine would NOT make up a base pair, as is the case with adenine and guanine.
This is illustrated in the below diagram, using correct pairings of nucleotides
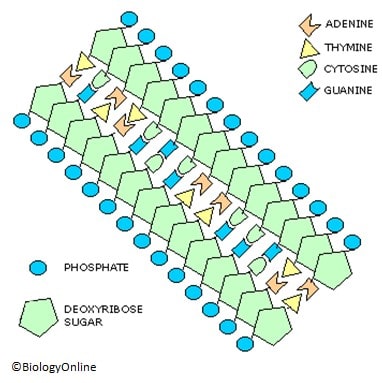
The diagram is two dimensional, remember that DNA is structured in a double helix fashion, as shown to the above right. This continuous sequence, and the sequence they are in determine an organisms’ structural, physical and anatomical features.
DNA Replication
Cells do not live forever, and in light of this, they must pass their genetic information on to new cells, and be able to replicate the DNA to be passed on to offspring. It is also required that fragments of DNA (genes) have to be copied to code for particular bodily function.
It is essential that the replication of it is EXACT. In order for replication to occur, the following must be available
- The actual DNA to act as an exact template
- A pool of relevant and freely available nucleotides
- A supply of the relevant enzymes to stimulate reaction
- ATP to provide energy for these reactions
When replicating, the double helix structure uncoils so that each strand of DNA can be exposed. When they uncoil, the nucleotides are exposed so that the freely available nucleotides can pair up with them.
When all nucleotides are paired up with their new partners, they re-coil into the double helix. As there are two strands of DNA involved in replication, the first double helix produces 2 copies of itself via each strand.
It is said that the replicated DNA is semi-conservative, because it possesses 50% of the original genetic material from its parent. These 2 new copies have the exact DNA that was in the previous one. This template technique allows genetic information to be passed from cell to cell and from parents to offspring.
The next tutorial looks at protein synthesis, and how genetic information in a DNA strand can be used to code for a particular protein.
 CELL – LABEL THE PARTS (pdf) | CELL – LABEL THE PARTS This worksheet is useful in helping the students assess their familiarity with the different parts of the cell, both the eukaryotic and the prokaryotic types. This is useful in genetics as it helps gauge the student’s knowledge of the difference between the two cell types, especially in terms of the location of the genetic material. Subjects: Genetics & Evolution, Cell Biology |
Test your knowledge: DNA Quiz
You will also like...

Seed Plants
Seed plants are vascular plants. They differ from the other vascular plants in producing seeds that germinate into a new..

A Balanced Vitamin Diet – Vitamins A – K
A balanced diet is essential to a healthy organism. Insufficiency or too much of a particular element or compound, such ..

Insects
There are more species of insects than any other species combined. This surely illustrates that insects have the selecti..

Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal ..
Primitive Animals
Life, as we know it today, is presumed to have started in the sea and many of them were likely eukaryotic animal-like or..
Biological Viruses
Viruses possess both living and non-living characteristics. This unique feature distinguishes them from other organisms...
