Freshwater Ecology

Freshwater ecology studies the relations of aquatic organisms to their freshwater habitats.
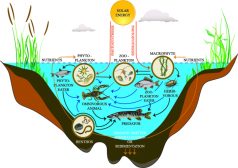
Freshwater ecology focuses on the relations of aquatic organisms to their freshwater habitats. There are two forms of communities that thrive in freshwater: the lentic and the lotic communities. In these communities, plants and animals evolved special characteristics that make them better adapted to their habitat. Get to know more about these features and the various factors, both biotic and abiotic, surrounding them.
Objectives
- To recognize the major constituents of freshwater ecosystem
- To distinguish the lentic from lotic communities and their distinctive features that made them suitable to their respective habitats and ecological niche
- To identify the abiotic and biotic factors and how they help shape the communities in a freshwater ecosystem
Key Points
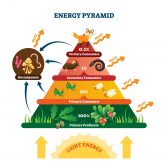
- An ecological pyramid indicates how energy is passed along from the autotrophs to the carnivores. The reliance of organisms to other organisms affect the way they obtain energy for use in propagation and survival.
- Abiotic factors, especially sunlight, are a great predictor of a freshwater community. Plants, for instance, rely on the quality and the quantity of light available. Herbivores, in turn, depend on the abundance of primary producers in the food chain. Subsequently, carnivores and omnivores are affected as well.
- All aquatic life are ectotherms, meaning their body temperature varies directly with its environments.
- In terms of plant diversity, lentic communities are more diverse than lotic communities. A still body of water provides less harsh condition for the survival of many plant species.
- One of the main differences between lotic and lentic communities is that the water is moving at a particular velocity in lotic communities. This can, therefore, influence what type of organisms can occupy the ecosystem.
- As with plants, animals in freshwater ecosystems have also acquired evolutionary adaptations.
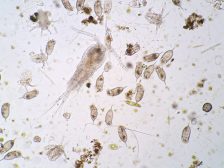
- Planktons (phytoplankton and zooplankton) are microscopic organisms that live and thrive in great number in aquatic habitats.
Freshwater Producers and Consumers
Freshwater ecosystem is comprised of four major constituents, namely elements and compounds, plants, consumers, and decomposers. Read this tutorial to learn about each of them and their role in a freshwater ecosystem…
Freshwater Community Energy Relationships – Producers & Consumers
This tutorial looks at the relationship between organisms. It also explores how energy is passed on in the food chain and ecological pyramids…
Abiotic and Biotic Factors
This tutorial deals with the abiotic factors of the freshwater environment that determine what sort of life would be suited to living and adapting to the conditions of the ecosystem…
Abiotic Factors – Water Conditions
A still body of water may be disturbed by a variety of factors. One of them is wind. In fact, it is considered as the prime factor responsible for water disturbance. Such disturbance can affect the distribution of organisms in the habitat. This tutorial looks at how these abiotic factors affect the way in which organisms operate in the freshwater ecosystem…
Freshwater Communities & Lentic Waters
Lentic or still water communities can vary greatly in appearance — from a small temporary puddle to a large lake. The size and depth of a still body of water are major factors in determining the characteristics of that ecosystem. Learn in this elaborate tutorial how life thrives in and influenced by a still-water habitat…
Still Water Animals
Animals living in aquatic habitats have diversified and evolved through time. They eventually occupy ecological niches available in the ecosystem. Three regions exist in a freshwater environment: profundal, pelagic, and benthic. Get more information on each of these regions and how these regions led to the varying niches that freshwater animals eventually occupied…
Freshwater Lentic Communities & Animals
This tutorial looks at some of the communities in freshwater lentic habitats. For instance, symbiosis occurs in a community of hydrophytes providing a substrate for algae. In return, the algae prevent excessive herbivory of hydrophytes by serving as food to the herbivores. Know more details here…
Still Freshwater & Plants
Plants in lentic habitats have features not found in terrestrial plants. They acquired these features as they adapt to this type of habitat. Read this tutorial to learn more…
Still Water Community Plants
This tutorial looks at the adaptations of freshwater plants for them to thrive in still water habitats. Familiarize yourself with these various adaptations as well as their nutritional requirements obtained not from the soil but from freshwater…
Running Water Freshwater Communities
This tutorial introduces flowing water communities, which bring new and dithering factors into the equation for possible species occupying the area. Read to know more…
Running Water Freshwater Community Factors
This tutorial noted some of the physical and chemical factors that provide the framework of a running water community in which organisms in their favored ecological niches occupy. Learn how each of these factors affects lotic communities in this tutorial…
Lotic Communities & Algae
Lotic communities have conditions that are rather harsh for typical plants. Thus, the diversity of plant species in lotic habitats is smaller than in lentic habitats. Find out why in this tutorial…
Lotic Communities & Animals
A running water environment offers numerous microhabitats for many types of animals. Similar to plants, animals in lotic communities have acquired evolutionary adaptations to better suit this running water environment. Know more about their evolutionary adaptations in this tutorial…
Freshwater Communities & Plankton
Planktons are microscopic organisms that live suspended in aquatic habitats. There are two groups: the phytoplanktons and the zooplanktons. Learn the differences between the two in this tutorial…
Pollution in Freshwater Ecosystems
There are many environmental factors that arise due to the usage of water in one way or another and for every action that man does, there is a resultant effect on the ecosystem. In this tutorial, some scenarios where human action results in a response from the ecosystem, either physically or chemically, are described. ..