Human Biology – Food and Digestion
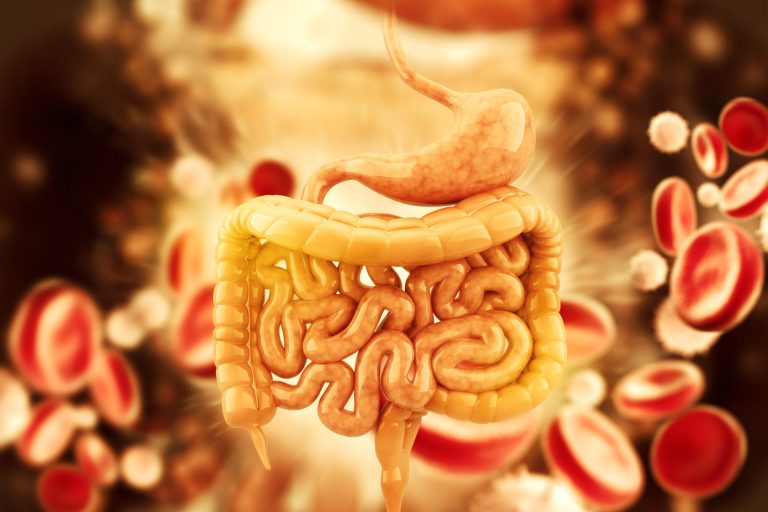
Human gastrointestinal tract
Food is what is required by humans to grow and survive, and provide a ‘fuel’ for the energy needed in our biological reactions
As opposed to plants that can acquire their food from the soil and sunlight, animals are required to eat foodstuffs in order to create the energy they need to survive. These foods contain many compounds and elements that are useful to our body and our daily functions.
This food is entered into the body via the mouth, where enzymes such as lysozyme begin to breakdown the food while it is chewed. When this food is broken down into smaller pieces it can then be swallowed, where it travels down the esophagus towards the stomach.
The stomach then continues to break down the foodstuff. The stomach at this point is filled with a type of acid that further breaks down the food until it is in a semi-liquid state. Note that the stomach only acts as a storage point at this stage, until the food slowly passes into the duodenum, which is part of the small intestine. It is here where the food is completely broken down, in the following manner:
- Proteins are broken down into amino acids
- Fats into fatty acids
- Complex sugars into simple sugars
From here, you can see that a complex product (the food you eat) is stripped bare, until the substances that they are broken down to can be used by the body in some way. By breaking down these foodstuffs to their most basic nature, the body can then rebuild these substances as and when required, for example, to create enzymes.
The body can then use these substances when they are in demand, such as raising blood sugar levels in the bloodstream so that energy can be created in the cells around the body via respiration.
The Sugar Homeostasis tutorial in the Regulation of Biological Systems looks at how the body determines when a particular action is required, such as the increase of blood sugar concentration. Also, the Cell Biology Tutorial ADP and ATP introduces ATP, the body’s biological energy, and how it is created.
In order for the body to successfully utilize the energy available within the food and use it properly, humans must intake the required amount of nutrients and minerals that our body requires; this can be done by having a balanced diet. A good diet will consist of the right measurement of the following compounds.
- Vitamins – Vitamins are required for various chemical reactions in the body. They can be found mostly in dairy products, fruits, and vegetables.
- Proteins – Proteins are also vitally important as part of a balanced diet. Proteins have many functions such as globular proteins in the body which make enzymes, hormones and antibodies, for example, all essential to human existence
- Carbohydrates – Carbohydrates are compounds that consist of carbon (carbo-), hydrogen (-hydr-) and oxygen (-ate) atoms. Glucose, the compound that is broken down in the first step of respiration is an example of a carbohydrate, hence the importance of carbohydrates in diets.
- Fats – Also known as lipids, fats produce twice the amount of energy that carbohydrates are capable of producing, and this is due to the more complex nature of their structure. There are five different types of lipid, either, triglycerides, phospholipids, glycolipids, steroids and waxes
- Minerals – These inorganic substances are required for a variety of reasons in the body. One such example is the requirement of iron, which is present in hemoglobin, in its role of absorbing oxygen from the lungs into the bloodstream.
The right measurement of the above compounds in our daily diet leads to an optimally functioning body, which has all the building blocks it needs to execute cellular processes on a day to day basis.
Such a balanced diet also helps combat disease and provide the optimal conditions for our body to operate and grow. If this is not the case, a deficiency in a particular substance can lead to disease.
Some of the diseases associated with an unbalanced diet are investigated in the next tutorial.
You will also like...
Birth of a Human Baby
Following nine months inside the mother's womb is the birth of the baby. Know the different stages of the birthing proce..

Early Mammals on Earth
The Earth's ecosphere was rapidly changing and throwing up a wide range of ecological niches that new adaptive organisms..
Freshwater Communities & Plankton
Planktons are microscopic organisms that live suspended in aquatic habitats. There are two groups: the phytoplanktons an..

Gibberellins and Gibberellic Acid
This tutorial describes the role of gibberellin family in plants. Find out the effects of gibberellin on plant growth an..

Selective Breeding
Gregor Mendel's studies into Monohybrid and Dihybrid crossing and Charles Darwin's study of evolution and natural select..
Temperature Regulation in Animals
This tutorial elucidates body temperature regulation. Know the details here to learn how the body sets the body temperat..
