Human Perception – Neurology
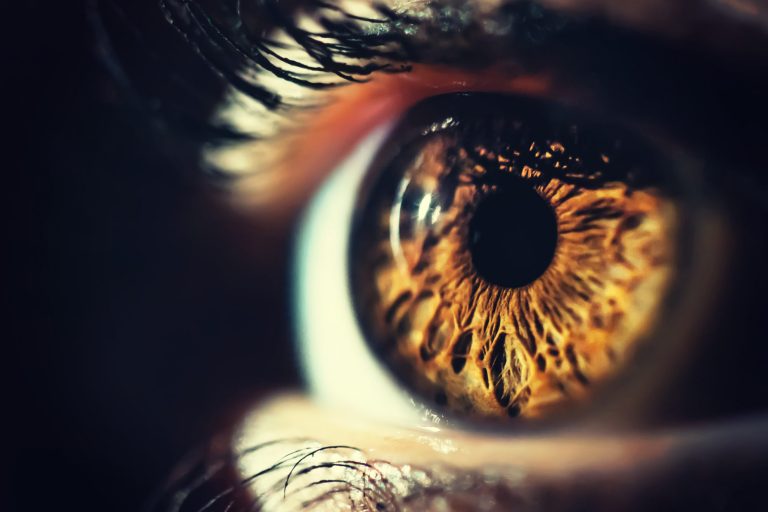

Human perception in action
Table of Contents
A better understanding of human perception unlocks the key to how the mind works, an advantage when working with people with mental disorders.
Visual Perception
The below diagram is an illustration as to how we all perceive things in our own way, as suggested by the theories of Jung and Freud.

Human Perception in Action
What do you see? Some of you may see 2 green faces, others may see a white chalice. This all depends on your initial perception of the diagram. You may find that when you look again you may see the alternate picture within the diagram.
The retina is responsible for interpreting visual stimuli such as this. It picks up photons of light via the 130 000 000 rods and cones situated on it. In pre-modern times it was considered that visual perception simply encompassed what was seen by the eye on the outside. These external stimuli would, in turn, produce a perception in the brain caused by the stimulus.
However, this is not the case. Modern medicine now knows that information from the eye is simply a physiological process that does not actually process the signals it receives. This job is left to the brain.
The senses simply act as a messenger to a particular stimulus that is seen. The brain is the place where external stimuli are actually perceived.
Spatial Awareness
The environment we live in is 3 dimensional, thus needs a 3-dimensional approach to understand it. Therefore height, width, and depth must be measured by the eyes.
This is possible by the way the eyes are situated on the head. Positioned either side of the nose, the right eye picks up a vision on the left hemisphere and the left eye picks up vision in the right hemisphere.
The images picked up by the eyes are projected upside down on each of the eyes’ retina. This, in turn, will be perceived as the right way up by the brain, which will interpret the three-dimensional values of the external environment at a very fast and effective rate.
Illusions
It is possible for the physiological state of the brain to deviate from the norm and trigger of a mental disorder. Illusions are a symptom of such mental disorders. However, it is also possible to trick the senses of a perfectly functional healthy brain. Illusions, such as the mirages that appear in the desert are caused by the trickery of the sense, leading us to believe there is something out there when this is not the case.
More information on illusions and mind trickery is looked upon in the next tutorial, Neurology of Illusions.
You will also like...

Indicator Species and Endangered Species
Certain species are capable of expressing characteristics indicative of the state of the ecosystem they occupy. They are..

Roots
This study guide tackles plant roots in greater detail. It delves into the development of plant roots, the root structur..

Origins of Life on Earth
Earth was created around 4.5 billion years ago and life began not long after. Primitive life likely possessed the elemen..

Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
This tutorial deals with the structure and function of flowers, fruits, and seeds. Also included here are the types of f..

Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal ..
Birth of a Human Baby
Following nine months inside the mother's womb is the birth of the baby. Know the different stages of the birthing proce..
