Independent Assortment and Crossing Over
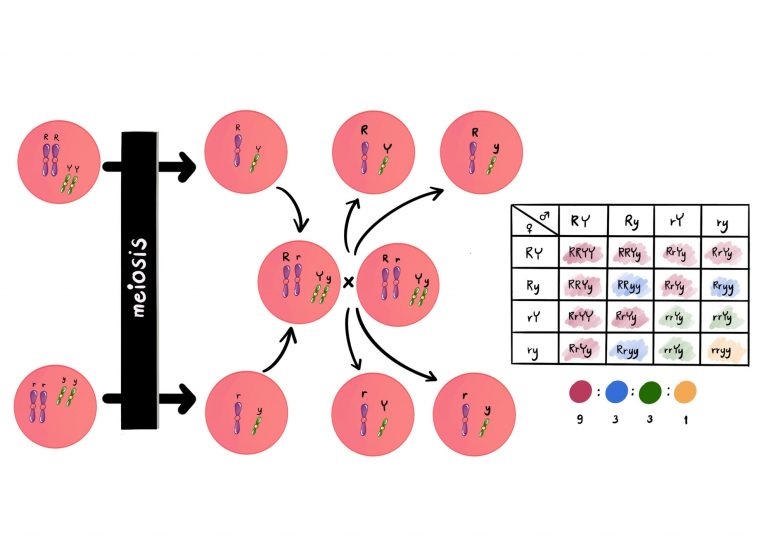
A schematic diagram implying independent assortment
Table of Contents
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.
The previous tutorial investigates the process of meiosis, where 4 haploid gametes are created from the parent cell. Half the genetic information from a parent is present in these haploids, which fuse with gametes of the opposite sex to create a zygote, with a complete chromosome complement that will create offspring after prolonged growth.
The process of meiosis increases genetic diversity in a species. The sex organs which produce the haploid gametes are the site of many occurrences where genetic information is exchanged or manipulated.
Independent Assortment of Chromosomes
Alleles for a particular phenotype determine what characteristic an organism will express, as with the following example where
- Chromosome 1 contains an allele for blonde hair
- Chromosome 2 contains an allele for brown hair
- Chromosome 3 contains an allele for blue eyes
- Chromosome 4 contains an allele for brown eyes

The top assortment to the left produces 2 blonde hair/blue eyes gametes while the below produces 2 brown hair/brown eyes gametes

The top assortment on the right produces 2 blonde hair/brown eyes gametes while the below produces 2 brown hair/blue eyes gametes
The above indicates that even though the two homologous chromosomes contain the same genetic information, the assortment of the chromosomes (the order they lie in) can determine what genetic information is present in each of the 4 gametes produced. With 23 chromosomes in a human gamete, there are 223 combinations (8388608 combinations)
Credit: Biology Professor
Crossing Over
During meiosis, when homologous chromosomes are paired together, there are points along the chromosomes that make contact with the other pair. This point of contact is deemed the chiasmata and can allow the exchange of genetic information between chromosomes. This further increases genetic variation.
There are also many other ways in which genetic variation is increased in a species gene pool, all of which are described in the following pages.
The next tutorial investigates the work of Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk famous for his work involving monohybrid and dihybrid crossing, alongside the continuation into looking at genetic diversity through meiosis and genetics in general.
 | CROSSING OVER & INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT – QUIZ Use this to evaluate the student’s familiarity with the core concepts in crossing over and independent assortment. It has two sections. The first is a fill-in-the-gaps test about crossing over and the second is a matching type about Mendelian Law of Independent Assortment. Subjects: Genetics & Evolution |
You will also like...

Freshwater Communities & Lentic Waters
Lentic or still water communities can vary greatly in appearance -- from a small temporary puddle to a large lake. The s..

The Origins of Life
This tutorial digs into the past to investigate the origins of life. The section is split into geological periods in the..

Mammalian Ancestors
Mammals are a diverse group of organisms, where most of them develop their offspring within the uterus of the mother. Ov..
Growth and Development of a Human Baby
Upon fertilization, a zygote forms and develops into an embryo. This tutorial elaborates on the growth and development f..

Still Water Animals
Animals living in aquatic habitats have diversified and evolved through time. They eventually occupy ecological niches a..
Temperature Regulation in Animals
This tutorial elucidates body temperature regulation. Know the details here to learn how the body sets the body temperat..
