Meiosis and Alternation of Generations
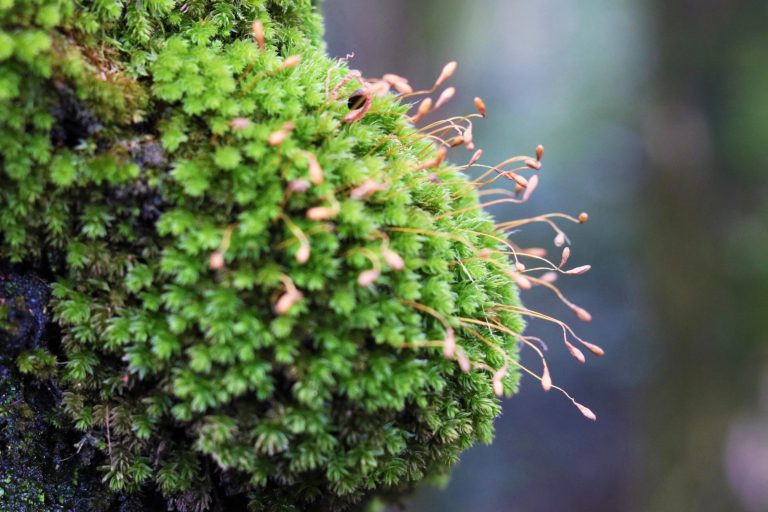

A moss plant (bryophyte) sporophyte and gametophyte generations.
Table of Contents
Review of Mitosis: Cell Cycle
The cell cycle contains the process in which cells are either dividing or in between divisions. Cells that are not actively dividing are said to be in interphase, which has three distinct periods of intense activity that precedes the division of the nucleus, or mitosis. The division of the rest of the cell occurs as an end result of mitosis and this process occurs in regions of active cell division, called meristems. Meristems will be looked at in the plant tissue tutorial.
Mitosis is a process within the cell cycle that is divided into four phases which we will sum up here:
- Prophase—the chromosomes and their usual two-stranded nature becomes apparent, the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase—the chromosomes become aligned at the equator of the cell. A spindle composed of spindle fibers is developed and some attach to the chromosomes at their centromere.
- Anaphase—the sister chromatids of each chromosome, that is now called the daughter chromosomes, separate lengthwise and each group of daughter chromosomes migrates to the opposite ends of the cell.
- Telophase—the groups of daughter chromosomes are grouped within a developing nuclear envelope which makes them separate nuclei. A wall forms between the two sets of daughter chromosomes thus creating two daughter cells.
In plants, as the cell wall is developing, droplets or vesicles of pectin merge forming a cell plate that eventually will become the middle lamella of the new cell wall.
The key feature of mitosis is that the daughter cells have the same chromosome number and are otherwise identical to the parent cell.
Meiosis Introduction
Mitosis, as just reviewed above, is a process by which a cell can reproduce itself and the number of chromosomes and the nature of the DNA will be identical to the original parent cell. Very few species will grow or live indefinitely, so there must be some way to ensure the continuity of the species. Reproduction is the only way a species can be perpetuated, without perpetuation the species will become extinct. Reproduction can occur in several ways as vegetative propagation, such as in the development of runners in strawberry plants, or by special cells called vegetative spores which are products of mitosis. In these processes, the ‘offspring’ have identical cells and identical chromosomes to the parent cells and thus the processes are called asexual reproduction—a means without, so without sexual reproduction. Most plants, however, will undergo sexual reproduction which involves the production and recombining of sex cells called gametes. In flowering and cone-bearing plants, this involves the production of seeds. The gametes produced are male and female, and are called sperm cells and egg cells, correspondingly. When the gametes combine together, the cells fuse and form a single cell called a zygote. It is the zygote that will go on to become the plant embryo and eventually a mature, adult plant.
However, in thinking about this process, what would happen if both gametes had the same number of chromosomes as the rest of the cells in the organism? When they fused to become a zygote, they would have two times the number of chromosomes as the rest of the cells in the organism. The number of chromosomes would increase exponentially through the generations if this occurred. This is where meiosis comes in to play. Meiosis is the process by which gametes, sex cells, are formed. It is unique because gametes have exactly half of the total number of chromosomes as the rest of the cells in the parent organism. When two gametes, each with half the number of chromosomes, get together they are able to restore the chromosome number to the same as the rest of the cells in the parent organism. When the zygote develops into a plant embryo and eventually a mature plant, it will have the exact number of chromosome-specific to the species. Note that the processes and steps in meiosis are very similar to mitosis, so make certain you have a good understanding of mitosis so that you will be able to compare the two processes.
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of meiosis, keep in mind that all living cells have two sets of chromosomes—one from a male and one set from a female parent. The genes in the chromosomes may control the same characteristics but in contrasting ways—for example: genes for plant height, genes for plant color, genes for fruit color, etc—the female gamete might code for short plants, while the male gamete might code for tall plants. That is more of a genetics topic though. But you should know that the chromosomes that code for the same characteristics are called homologous chromosomes.
Phases of Meiosis
The end result of one round of meiosis will be four cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The daughter cells are rarely, if ever, identical to each other or the parent cell depending on the organism involved. There are two successive divisions in meiosis, which in plants occur without a pause. Mitosis takes roughly 24 hours, while meiosis takes up to two weeks. In some organisms, meiosis takes weeks or years depending on the organism.
Division I –Reduction division
The chromosome number is reduced to half the parent cell chromosome number. End result of division one is two cells.
Prophase I—Main features
- Chromosomes coil, becoming shorter and thicker, the two-stranded nature becomes apparent, two strands are called a chromatid and chromosomes are aligned in pairs. Each pair of chromosomes has four chromatids and they have a centromere attached in the center holding the four strands together.
- Nucleolus disassociates and nuclear envelope dissolves.
- Segments of the closely associated pairs of chromatids may be exchanged with each other (between the pair members) this is called crossing-over. Each chromatid contains the original amount of DNA but now may have “traded” genetic material.
- The chromosomes separate. Some spindle fibers are forming and some are attaching to the centromeres of the chromosomes. The fibers extend from each pole of the cell.
Metaphase I—Main features
- In pairs, the chromosomes align at the equator of the cell, with the centromeres and spindle fibers apparent.
- The two chromatids, from each chromosome, function as a single unit.
Anaphase I—Main features
- One entire chromosome, consisting of two chromatids, migrates from the equator to a pole. The chromosomes do not separate from each other and retain both chromatids when the reach their pole. At each pole, there will be half the chromosome number. If crossing over occurred in prophase then the chromosomes will consist of original DNA and DNA from a homologous chromosome—now at the opposite pole.
- The centromere remains intact in each pair of chromatids.
Telophase I—Main features
- What occurs in this step, depends on the species involved, as they may revert to interphase or proceed directly to division II.
- If they revert to interphase, they will only do so partially and the chromosomes will become longer and thinner.
- Nuclear envelopes will not form, but the nucleoli will generally recluster.
- Telophase is over when the original cell becomes two cells or two nuclei.
Division II—Equational division
The chromosome number stays the same, the cells replicate and result in four cells. The events closely resemble the events in mitosis, except that there is no duplication of DNA during the interphase that may or may not occur between the two divisions.
Prophase II—Main features
- Chromosomes of both nuclei become shorter and thicker. The two-stranded nature becomes apparent once again.
Metaphase II—Main features
- Chromosomes align their centromeres along the equator.
- Spindle fibers form and attach to each centromere, extending from one pole to the other.
Anaphase II—Main features
- The centromeres and chromatids of each chromosome separate and begin their migration to the opposite poles.
Telophase II—Main features
- The coils of chromatids—now called chromosomes again—relax and the chromosomes become longer and thinner.
- Nuclear envelopes and nucleoli reform for each group of chromosomes.
- New cell walls form between the four groups of chromosomes.
- Each set of chromosomes in the four new cells has exactly half of the chromosome number of the original number.
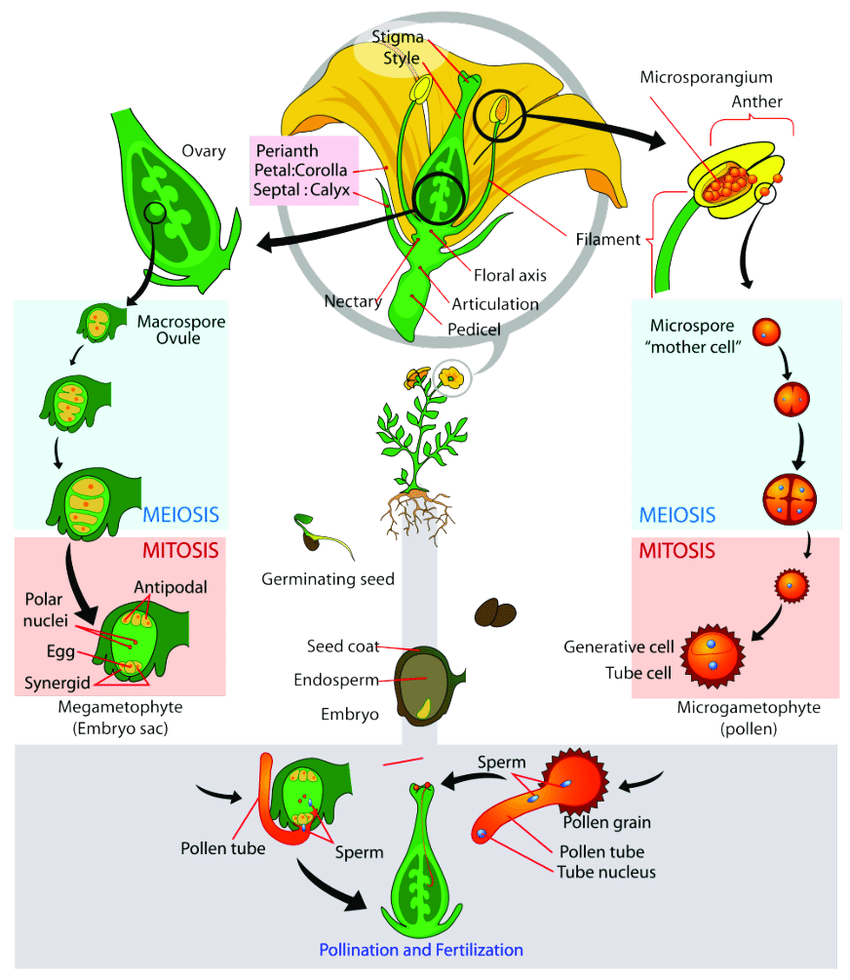
Alternation of Generations
One member of every original pair of chromosomes end up in each resulting cell, which means each cell has one set of chromosomes. None of the daughter cells is identical to the parent cell. A cell with one set of chromosomes is called haploid and a cell with two sets is called diploid. In sum, a diploid cell undergoes meiosis and results in four haploid cells.
Sex cells, or gametes, of an organism, are haploid and when a zygote is formed, the zygote is diploid. This is always true, no matter how many chromosomes an organism might have. In many places, you will find it stated that an organism has n number of chromosomes. In this case, an organism will have 2n chromosomes in its diploid cells and 1n chromosomes in its haploid cells. Alternation of generations refers to a plant’s life cycle including sexual reproduction that is characterized by alternating between a diploid (2n) sporophyte phase and a haploid (1n) gametophyte phase.
You will also like...

Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
The kidneys are responsible for the regulation of water and inorganic ions. Read this tutorial to learn about the differ..

Chemical Composition of the Body
The body is comprised of different elements with hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen as the major four. This tutorial..

Plant Tissues
Plant organs are comprised of tissues working together for a common function. The different types of plant tissues are m..

The Gene Pool and Population Genetics
According to Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection, preferable genes are favored by nature in the gene pool, and ..
Chromosome Mutations
Mutations can also influence the phenotype of an organism. This tutorial looks at the effects of chromosomal mutations, ..

Human Reproduction
Humans are capable of only one mode of reproduction, i.e. sexual reproduction. Haploid sex cells (gametes) are produced ..
