Mendel’s Law & Mendelian Genetics
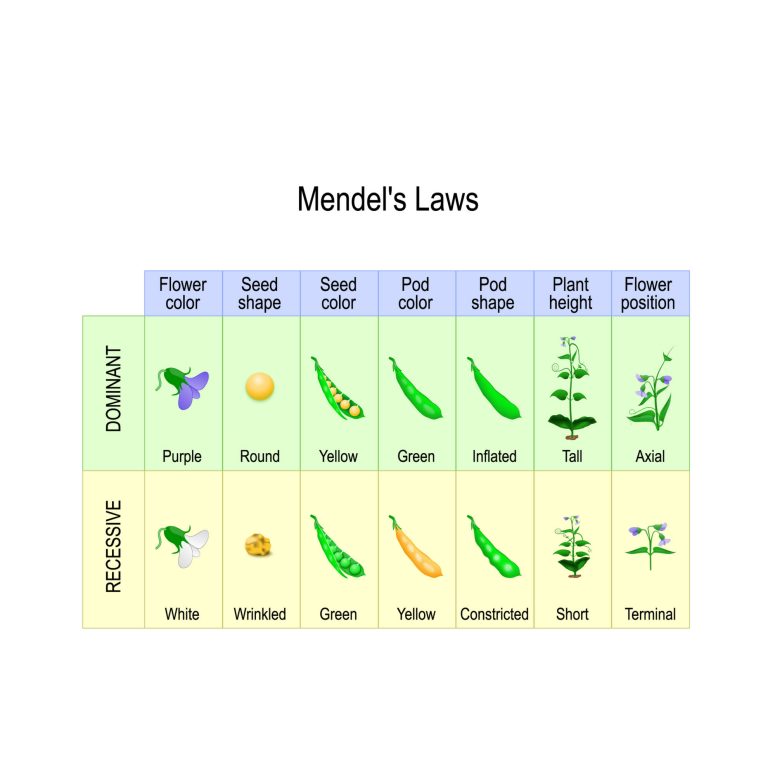
A chart depicting Mendel’s Law of Dominance
Table of Contents
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.
The previous tutorial, Dominance, has described Gregor Mendel’s law of dominance. In this tutorial, you will learn another Mendel’s law — the principle of segregation.
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
“The alleles of a gene exist in pairs but when gametes are formed, the members of each pair pass into different gametes. Thus each gamete contains only one allele of each gene.”
Example of a Cross
The following dihybrid cross involves two true-breeding pea plants, where two factors are looked at, the shape of the seed and the color of the seed.
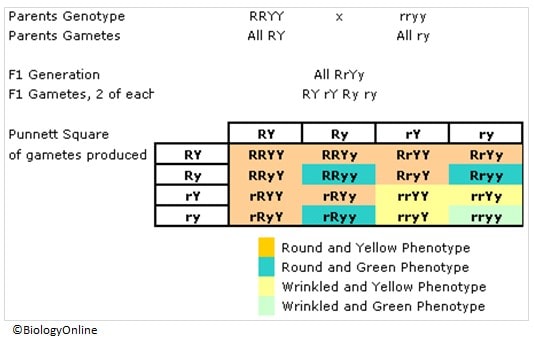
More examples of dihybrid cross here.
Summary of Mendelian Genetics
The past few pages have elaborated on the work of Gregor Mendel and how his work has paved the way for predicting the characteristics of offspring. However, a degree of randomness is involved, when involving factors such as independent assortment during meiosis and the possibility of genetic mutations (explained in further pages).
In light of this, Mendel’s work allowed us to see that there is a degree of genetic inheritance from parents in offspring though modern biology indicates that more factors come into play to determine the final genotype and phenotype of an organism.
Sticking to the subject of genetics, the next tutorial looks at sex determination via chromosomes X and Y and some of the genetic traits inherited via these two chromosomes.
 | MENDEL’S PRINCIPLES OF HEREDITY – QUIZ Print this quiz for your students to answer. The first part is a recall of Gregor Mendel’s principles of heredity. The second part is a multiple-choice test about alleles and sex chromosomes. Subjects: Genetics & Evolution |
You will also like...

Circulation
The circulatory system is key to the transport of vital biomolecules and nutrients throughout the body. Learn about the ..

Lotic Communities & Animals
A running water environment offers numerous microhabitats for many types of animals. Similar to plants, animals in lotic..

Early Mammals on Earth
The Earth's ecosphere was rapidly changing and throwing up a wide range of ecological niches that new adaptive organisms..

Still Freshwater & Plants
Plants in lentic habitats have features not found in terrestrial plants. They acquired these features as they adapt to t..

Running Water Freshwater Community Factors
This tutorial noted some of the physical and chemical factors that provide the framework of a running water community in..

Stems
Stems primarily provide plants structural support. This tutorial includes lectures on the external form of a woody twig ..
