Photosynthesis – Photolysis and Carbon Fixation
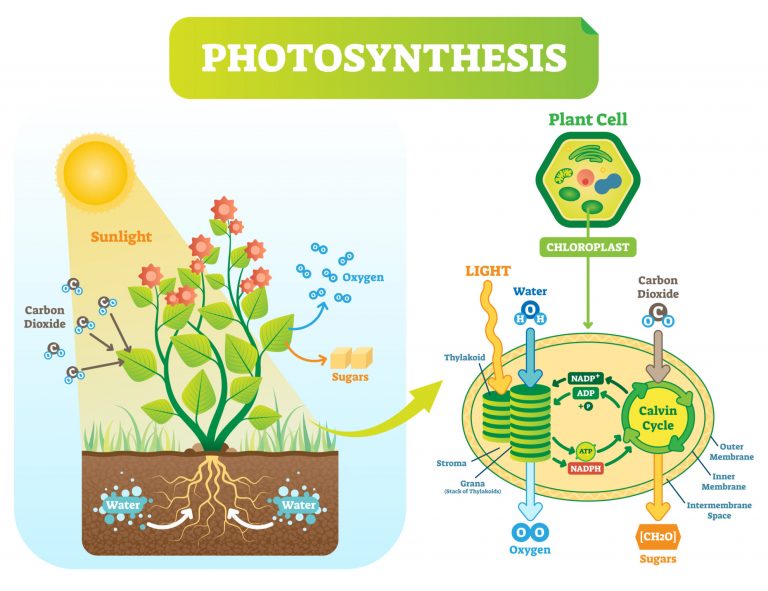
The process of photosynthesis
Table of Contents
Photosynthesis is the means that primary producers (mostly plants) can obtain energy via light energy. The energy gained FROM light can be used in various processes mentioned below for the creation of energy that the plant will need to survive and grow.
Photosynthesis is a reduction process, where hydrogen is reduced by a coenzyme. This is in contrast to respiration where glucose is oxidized.
The process is split INTO two DISTINCT areas, photolysis (the photochemical stage) and the Calvin Cycle (the thermochemical stage). The diagram below gives a summary of the reaction, where light energy is used to initiate the reaction in its presence;
CO2 + H2O > glucose + oxygen
Photolysis
This part of photosynthesis occurs in the granum of a chloroplast where light is absorbed by chlorophyll; a type of photosynthetic pigment that converts the light to chemical energy. This reacts with water (H2O) and splits the oxygen and hydrogen molecules apart.
From this dissection of water, the oxygen is released as a by-product while the reduced hydrogen acceptor makes its way to the second stage of photosynthesis, the Calvin cycle.
Overall, since the water is oxidized (hydrogen is removed) and energy is gained in photolysis which is required in the Calvin cycle
The Calvin Cycle
Also known as the carbon fixation stage, this part of the photosynthetic process occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts. The carbon made available FROM breathing in carbon dioxide enters this cycle, which is illustrated below:
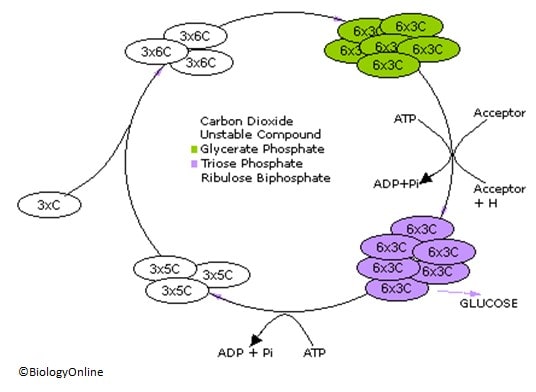
Just like the Kreb’s Cycle in respiration, a substrate is manipulated INTO various carbon compounds to produce energy. In the case of photosynthesis, the following steps occur, which create glucose for respiration FROM the carbon dioxide introduced INTO the cycle;
- Carbon FROM CO2 enters the cycle combining with Ribulose Biphosphate (RuBP)
- A compound formed is unstable and breaks down FROM its 6 carbon nature to a 3 carbon compound called glycerate phosphate (GP)
- Energy is used to break down GP INTO triose phosphate, while a hydrogen acceptor reduces the compound, therefore, requiring energy
- Triose Phosphate is the end product of this, a 3 carbon compound which can double up to form glucose, which can be used in respiration.
- The cycle is completed when the leftover GP molecules are met with a carbon acceptor and then turned INTO RuBP, which is to be joined with the carbon dioxide molecules to re-begin the process.
The energy that is used up in the Calvin cycle is the energy that is made available during photolysis. The glucose that is made via GP can be used in respiration or a building block in forming starch and cellulose, materials that are commonly in demand in plants.
Limiting Factors in Photosynthesis
Some factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in plants, as follows
- Temperature plays a role in affecting the rate of photosynthesis. Enzymes involved in the photosynthetic process are directly affected by the temperature of the organism and its environment
- Light Intensity is also a limiting factor, if there is no sunlight, then the photolysis of water cannot occur without the light energy required.
- Carbon Dioxide concentration also plays a factor, due to the supplies of carbon dioxide required in the Calvin cycle stage.
Overall, this is how a plant produces energy which supplies a rich source of glucose for respiration and the building blocks for more complex materials. While animals get their energy FROM food, plants get their energy FROM the sun.
The next tutorial investigates DNA structure and replication…
You will also like...

Non-Mendelian Inheritance
In this tutorial, find out more about certain types of inheritance that does not follow the Mendelian inheritance patter..
Homeostasis of Organism Water Regulation
Osmoregulation is the regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream, effectively controlling the amount of water..
Growth and Development of a Human Baby
Upon fertilization, a zygote forms and develops into an embryo. This tutorial elaborates on the growth and development f..

Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Molecules move within the cell or from one cell to another through different strategies. Transport may be in the form of..

Lotic Communities & Algae
Lotic communities have conditions that are rather harsh for typical plants. Thus, the diversity of plant species in loti..

Bryophytes
Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) are a plant group characterized by lacking vascular tissues. They include the mosses, th..
