Running Water Freshwater Communities
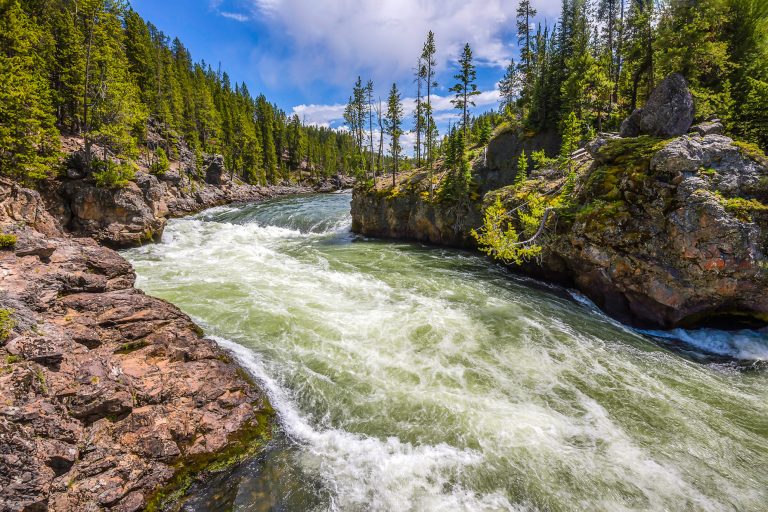

River, a running water freshwater habitat
Running water freshwater communities are also known as lotic communities, lotic meaning running water. Lotic communities are formed by water being introduced to the freshwater body from a variety of sources:
- Rainfall – A percentage of water in the running water community will be present as a result of rainfall directly entering it.
- Ground Surface Water – Deriving from previous rainfall, water will enter the running water community.
- Underground Water – Water absorbed into the soil can also enter.
- Water Table – Deep underground there is a ‘water table’ which can also provide water for the running water community.
There are also many other, less significant ways water can enter the stream, for example, due to man-made interference such as an outlet pipe, or water transpired by plants in the nearby area.
The accumulation of this water from the areas mentioned above also introduces essential minerals and nutrients that are ideal for plant growth, the primary producers of a community. With that in hand, alongside an abundance of water, pioneers can occupy the running water environment.
One of the main differences between lotic and lentic communities is the fact that the water is moving at a particular velocity in lotic communities. This can have great bearing on what organisms occupy the ecosystem and what particular ecological niche they can exist in.
Running water can bring many factors into play affecting the lives of the organisms in this particular environment:
- The movement of minerals and stones caused by the velocity and volume of the water means the water bed is constantly changing. The faster and higher volume of water present will result in a direct increase in the amount and size of particles shifted downstream.
- Standing waves are used by salmon at the bottom of waterfalls to spurn them upstream. At the same time, they cause small air pockets caused by oxygen replacing the splashing water, which results in a small micro-habitat becoming available suited to particular organisms
- Erosion is caused by the running water breaking down the river bank and beds, causing the geography of the river to change over a long period of time. This means that hydroseres previously occupying the river bank may find themselves distanced from the running water for example, and over time this would mean the overall ecosystem would change over time.
Such factors play a vital role in determining the overall chemical, physical and biological face of the running water ecosystem. We shall look at these physical and chemical differences that make up a running water ecosystem that will inevitably affect the biological make-up of the freshwater ecosystem. This is continued in the next tutorial.
You will also like...
The Human Physiology
Physiology is the study of how living organisms function. Thus, human physiology deals specifically with the physiologic..

Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal system breaks down particles of ingested food into molecular forms by enzymes through digestion and..

Ecosystem Succession
If the balance of nature is left untouched, landscapes can change dramatically over time. A previous ecosystem is supers..
Physiological Homeostasis
Homeostasis is essential to maintain conditions within the tolerable limits. Otherwise, the body will fail to function p..
Birth of a Human Baby
Following nine months inside the mother's womb is the birth of the baby. Know the different stages of the birthing proce..

Plant Water Regulation
Plants need to regulate water in order to stay upright and structurally stable. Find out the different evolutionary adap..
