The Homo Species
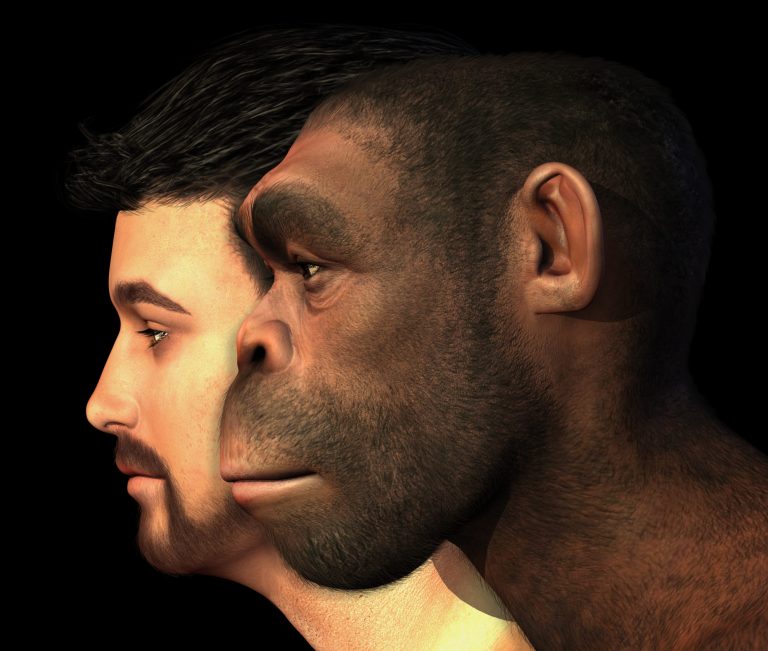

An artistic rendition of a modern human and a “Homo Erectus” side by side
Table of Contents
Over the long term, it looked like Homo would supersede any ‘similar model’ of animals due to their unique tool using competitive advantages. At this point in the timeline, Homo habilis was man’s link in that time and place and was typically taller than any of the australopithecines mentioned previously.
Homo erectus
Homo erectus is the Latin meaning for ‘upright man’. At around of the Quaternary Period of Phylogenetic classification, the Homo species was beginning to exhibit the characteristics of modern man. No doubt much of this had to do with their superiority over similar organisms in their ecological niche and the newer environments that early man was beginning to occupy.
The brain size of Homo erectus is notably larger than its ancestors, and excavations of the species have been found in parts of China, a long way away from the theoretical ancestral origins of man in Africa (or Europe, see previous).
Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens, meaning wise man was the next movement towards modern man. They existed as early as the Quaternary period (around 1.6 million years ago) and their brains showed increased growth from previous species and exhibited more intelligence from human records.
The tools being used were becoming more sophisticated, as were the learning and habituation over generations that allowed man to easily adapt to its surroundings. The species as a whole was occupying a diverse range of continents, therefore greatly diversifying our gene pool over a long period of time.
Archaeological finds have also suggested the first use of wooden tools, like spears, through various finds across the Asian, European and African continents.
Homo sapiens neanderthalensis is a subspecies of Homo sapiens well known for its hypothesized common ancestry with man. They arrived on the scene around a quarter of a million years ago and continued to evolve to around 30 000 BC. Due to the more recent nature of this subspecies, more information has been found out about them, although it is debatable whether the Neanderthal man and our own species are one of the same or unique.
The Neanderthals were widespread across both Europe and Asia during this time. From around the time that the Neanderthals were beginning to disappear, the new modern man was offering the newest competitive advantages and ability to adapt and learn. This species is our own, Homo sapiens sapiens.
Homo sapiens sapiens
From 30 000 years ago up until this present day, our own species has exhibited the most advantageous characteristics to adapt and manipulate our environment. The skills accumulated over many generations of our species and continued favoring of advantageous characteristics via natural selection inevitably meant that our species would evolve beyond all recognition in comparison to the other species of the planet.
From this point, the species and its component skills managed to colonize all the main continents of today’s world, bar Antarctica, which still presented conditions unbearable to the species and the technology of the time.
However, more complex tools were being developed, and that has continued over the period of time where we have successfully monitored historical events in our human race.
At this point, human history in an abstract manner truly begins.
You will also like...

A Balanced Vitamin Diet – Vitamins A – K
A balanced diet is essential to a healthy organism. Insufficiency or too much of a particular element or compound, such ..
Independent Assortment and Crossing Over
This tutorial describes the independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over as important events in meiosis. Read..

Biosecurity and Biocontrol
This lesson explores the impact of biosecurity threats, and why they need to be identified and managed. Examples to incl..
Adaptive Radiation
The diversification of several new species from a recent ancestral source, each adapted to utilize or occupy a vacant ad..

New Zealand’s Unique Fauna
Meet some of New Zealand's unique fauna, including endemic insects, frogs, reptiles, birds, and mammals, and investigate..

Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal ..
