The Human Nervous System
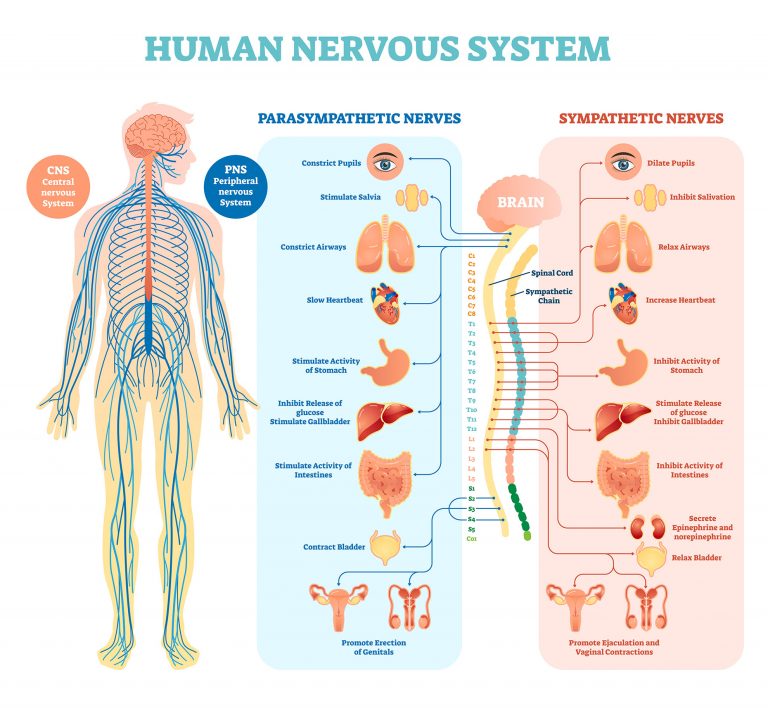
The human nervous system is comprised of the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Table of Contents
The nervous system is essentially a biological information highway, and is responsible for controlling all the biological processes and movement in the body, and can also receive information and interpret it via electrical signals which are used in this nervous system
It consists of the Central Nervous System (CNS), essentially the processing area and the Peripheral Nervous System which detects and sends electrical impulses that are used in the nervous system
The Central Nervous System (CNS)
The Central Nervous System is effectively the center of the nervous system, the part of it that processes the information received from the peripheral nervous system. The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is responsible for receiving and interpreting signals from the peripheral nervous system and also sends out signals to it, either consciously or unconsciously. This information highway called the nervous system consists of many nerve cells, also known as neurons, as seen below.
The Nerve Cell
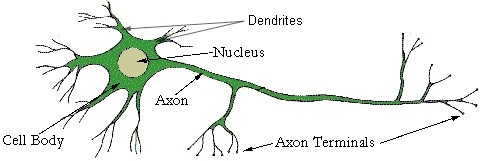
Each neuron consists of a nucleus situated in the cell body, where outgrowths called processes originate from. The main one of these processes is the axon, which is responsible for carrying outgoing messages from the cell. This axon can originate from the CNS and extend all the way to the body’s extremities, effectively providing a highway for messages to go to and from the CNS to these body extremities.
Dendrites are smaller secondary processes that grow from the cell body and axon. On the end of these dendrites lie the axon terminals, which ‘plug’ into a cell where the electrical signal from a nerve cell to the target cell can be made. This ‘plug’ (the axon terminal) connects into a receptor on the target cell and can transmit information between cells
The Way Nerve Cells Communicate
The “All-Or-None-Law” applies to nerve cell communication as they use an on / off signal (like a digital signal) so that the message can remain clear and effective from its travel from the CNS to the target cell or vice versa. This is a factor because just like electricity signals, the signal fades out and must be boosted along its journey. But if the message is either 1 or 0 (i.e. on or off) the messages are absolute.
Classification of Neurons
Interneurons – Neurons lying entirely within the CNS
Afferent Neurons – Also known as sensory neurons, these are specialized to send impulses towards the CNS away from the peripheral system
Efferent Neurons – These nerve cells carry signals from the CNS to the cells in the peripheral system
The next tutorial The Conscious & Unconscious Nervous System elaborates on how the nervous system works…
You will also like...

Growth and Plant Hormones
Plants, like animals, produce hormones to regulate plant activities, including growth. They need these hormones to respo..

Indicator Species and Endangered Species
Certain species are capable of expressing characteristics indicative of the state of the ecosystem they occupy. They are..

Mendel’s Law & Mendelian Genetics
One of Mendel’s law of inheritance is the “law of dominance”. Read this tutorial to know more about this form of i..

Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal system breaks down particles of ingested food into molecular forms by enzymes through digestion and..

Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory res..

Running Water Freshwater Communities
This tutorial introduces flowing water communities, which bring new and dithering factors into the equation for possible..
