The Origins of Life

Early life is presumed to begin in a so-called “primordial soup”
This tutorial digs into the past to investigate the origins of life. The section is split into geological periods in the form of a timeline. Find out how life arrived on Earth, why, and how living things evolved into their current diversities today.
Objectives
- To be familiar with the different geological periods and the major evolutionary events that transpired in each
- To gain an understanding how from one animal group to another gain dominion over a given geological time
- To be able to describe the events that support the theory of evolution occurring through natural selection.
Key Points
- The Earth existed around 4.5 billion years ago and life began to exist not long after. The first life forms were likely containing carbon as all living things possess this element.
- The early life forms on Earth continued to diversify. Eventually, single-celled organisms lived side by side with organisms comprised of multiple cells. The early multicellular animal-like organisms were presumed to be sponge-like.
- Animal life forms continued to diversify and eventually transitioned from a life in the sea to a life on land.
- Humans evolved later in the timeline. The dominance of modern man has continued to shape the future timeline of the planet Earth.
Tutorials
Origins of Life on Earth
Earth was created around 4.5 billion years ago and life began not long after. Primitive life likely possessed the element carbon within them. It is presumed that one of the family of compounds that first came up was the amino acids, the building blocks of protein. Over time, these life forms become more and more complex. Find out more about how life likely began on Earth…
Evolution of Life – Ancient Earth
Autotrophs flourished, absorbing carbon and light. Soon after, primitive life forms that could assimilate oxygen thrived. Life continued to diversify resulting in the rise of different organisms competing with one another for survival. Learn more about these single-celled life forms blossoming the primitive Earth…
The Evolution of Cell Organelles
The nucleus containing the genetic material, DNA, and the mitochondria, well-identified as the “powerhouse of the cell”, came about. This tutorial speaks of the evolution of organelles, their diversity, and similarity…
The Evolutionary Development of Multicellular Organisms
Multicellular organisms evolved. The first ones were likely in the form of sponges. Multicellularity led to the evolution of cell specializations that form tissues. Another major event was the evolution of sexual reproduction. The emergence of sex cells in the timeline provided a means for organisms to further diversify. Know more about these crucial events in geologic time in this tutorial…
Primitive Animals
Life, as we know it today, is presumed to have started in the sea and many of them were likely eukaryotic animal-like organisms. Because of the expanding diversity of animal life forms, taxonomists eventually came up with a classification scheme to group them into various phyla. Know more about the early animals that were likely the first ones to roam the ancient seas through this tutorial…
Arthropods
The arthropods were assumed to be the first taxon of species to possess jointed limbs and exoskeleton, exhibit more advanced receptors in the form of eyes, and develop various chemoreceptors. Since they possess such desirable features, their survival over the long term is apparent by their genetic diversity. Learn more elaborate details about arthropod evolution in this tutorial…
Insects
There are more species of insects than any other species combined. This surely illustrates that insects have the selective advantages that allow them to take the most advantage of the environment that they live in. Read more about the evolution of insects in this tutorial. Find out the reasons as to why insects enjoyed their continued existence over such a long period of time…
The Dinosaurs
Dinosaurs represented a major turn in the evolutionary development of organisms on Earth. The first dinosaurs were presumed to look a lot like the reptiles. As they continued to evolve, many of them became bigger and stronger. Read more about the evolution of dinosaurs and their subsequent extinction in this tutorial…
Mammalian Ancestors
Mammals are a diverse group of organisms, where most of them develop their offspring within the uterus of the mother. Over time, mammals have diversified into the placentals and the marsupials. Get a better understanding of how the mammals became dominant based on natural selection and geological events as elucidated in this tutorial…
Early Mammals on Earth
The Earth’s ecosphere was rapidly changing and throwing up a wide range of ecological niches that new adaptive organisms, such as mammals, could fit into. Eventually, every continent of the planet had its own variety of mammalian organisms and their own unique evolutionary chain and direction. Learn more about the early mammals that roamed the Earth alongside other organisms, such as reptiles, fish, and birds…
The Hominids
The hominid family diversified from the apes around 6 to 8 million years ago. Since then, the evolutionary path has proved to be nothing short of phenomenal. This tutorial elucidates the emergence of the hominid family from where the human ancestral line came from…
The Homo Species
The evolution of the species of the genus “Homo” led to the emergence of modern humans. Find out more about human evolution in this tutorial that elaborates on the different Homo species in the early geologic time.
..
Geological Periods
Geological periods is a study guide that cites the different geological periods on Earth’s timeline. Each has a brief overview and an outline of the tutorial guides that will help you track the history of life on Earth…
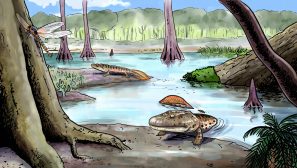
Amphibians & Early Reptiles
Obtaining air outside an aquatic environment required species to acquire suitable adaptations, and this was the case of amphibians. However, they were limited by their inability to inhabit drylands. Apparently, the early reptiles were able to do so. To learn more about the evolution of amphibians and reptiles, read this tutorial…